Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
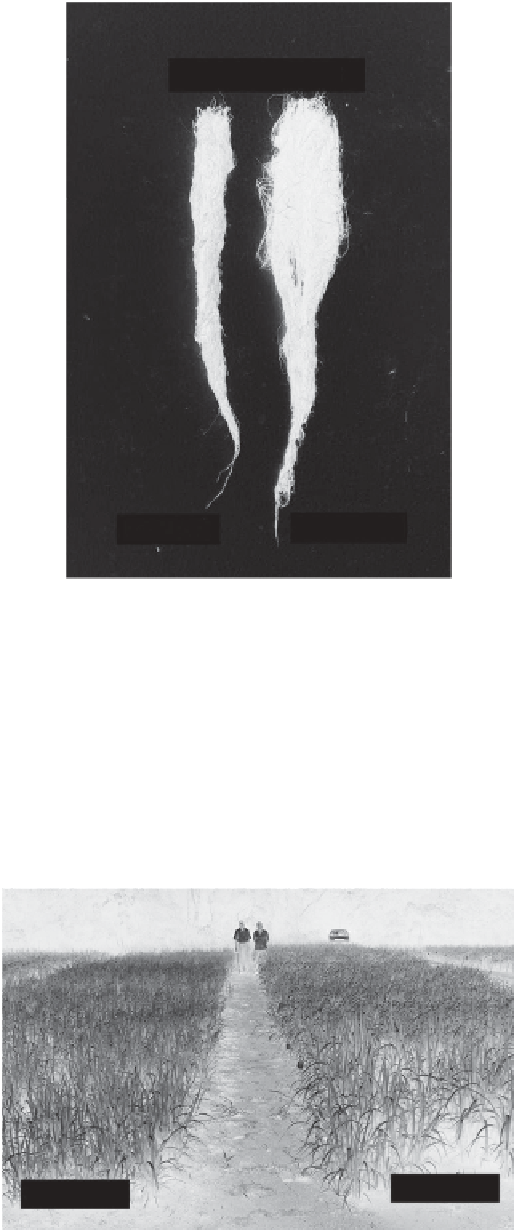
Mucuna cinereum
200 mg N kg
-1
0 mg N kg-1
FIGURE 3.8
Root growth of cover crop
Mucuna cinereum
at low and high N levels.
The influence of N on the growth of lowland rice tops and roots is presented in Figures 3.18 and 3.19.
Nitrogen deficiency in the tops of lowland rice genotypes is shown by a yellowing of the foliage of
plants that did not receive N. However, plants that received 300 mg N kg
−1
were green and having
larger foliage compared to plants that did not receive N. The growth of the roots of lowland rice
genotypes was also affected by N treatments (Figures 3.20 and 3.21). It was higher in the treatments
that received N compared to those that did not receive N.
Nitrogen deficiency has many adverse effects on a plant's physiological and biochemical pro-
cesses. In N-deficient plants, photosynthetic activity is decreased. Equally important to declining
With N
Without N
FIGURE 3.9
(
See color insert.
) Upland rice plot without N at the left and with N at the right grown on a
Brazilian Oxisol.