Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 3
Positions of
a
mn
of
h
m
a
where the distance
between the center and any
element is less than or equal
to 1. Note that the elements
on the horizontal axis are
overlapped. The resultant
derived filter with radius of
1 is shown in Figure 4(a).
and
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
h
mn
c
1
2
m
2
m
2
1
2
(
−
)
−
(
−
)
,
+
(
−
)
−
(
−
))
(
x
,
y
)=
a
mn
{−
δ
(
x
−
y
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
1
2
m
2
m
2
1
2
+
δ
(
x
−
(
)
−
(
−
)
,
y
+
(
)
−
(
−
))
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
1
2
(
−
m
2
)
−
m
2
)
−
1
2
(
−
δ
(
x
−
(
)
,
y
+
(
−
))
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
√
3
2
√
3
n
4
1
m
m
1
+
δ
(
x
−
2
(
2
)
−
(
)
,
y
+
(
2
)
−
2
(
))
},
(20)
where
m
=
0
,
1
,
2
,...
,
n
=(
m
%2
)(
2
k
+
1
)+((
m
+
1
)
%2
)
2
k
(
k
=
0
,
1
,
2
,...
)
and the
δ
-function is a common impulse function.
Point spread function
h
m
a
of the gradient filter with a radius of 1, which means
that every element of the filter is located at a distance from the center of the filter
less than or equal to 1, is illustrated in Figure 3.
To simplify notations, three functions
mn
mn
and
mn
, are defined as
η
,
η
η
√
3
2
a
mn
η
(
u
,
v
)
≡
sin
(
π
mu
)
cos
(
π
nv
)
(21)
√
3
2
√
3
4
1
2
u
3
4
u
b
mn
η
(
u
,
v
)
≡
sin
(
π
m
(
+
v
))
·
cos
(
π
n
(
−
v
))
(22)
√
3
2
√
3
4
1
2
u
3
4
u
mn
η
(
u
,
v
)
≡
sin
(
π
m
(
−
+
v
))
·
cos
(
π
n
(
+
v
))
(23)
The Fourier transforms of
h
a
,
h
b
and
h
c
are described by using
η
as follows:
)=
m
,
n
H
mn
m
,
n
a
mn
η
mn
H
a
(
u
,
v
(
u
,
v
)=
4
i
(
u
,
v
)
(24)
a
)=
m
,
n
H
mn
m
,
n
a
mn
η
mn
H
b
(
,
(
,
)=
(
,
)
u
v
u
v
4
i
u
v
(25)
b
)=
m
,
n
H
mn
m
,
n
a
mn
η
mn
H
c
(
u
,
v
(
u
,
v
)=
4
i
(
u
,
v
)
(26)
c














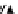




































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search