Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
hat-feature
: this binary feature indicates whether a delayed stroke has been re-
moved at the same horizontal position as the considered point.
•
•
speed
: the velocity is computed before resampling and then interpolated.
•
x-coordinate
: the
x
-position is taken after high-pass filtering, i.e., after subtract-
ing a moving average from the real horizontal position.
•
y-coordinate
: this feature represents the vertical position of the point after nor-
malization.
•
writing direction
: here we have a pair of features, given by the cosine and sine
of the angle between the line segment starting at the point and the
x
-axis.
•
curvature
: similarly to the writing direction, this is a pair of features, given by
the cosine and sine of the angle between the lines to the previous and the next
point.
•
vicinity aspect
: this feature is equal to the aspect of the trajectory (See Fig. 2)
•
vicinity slope
: this pair of features is given by the cosine and sine of the angle
of the straight line from the first to the last vicinity point (see Fig. 2).
•
vicinity curliness
: this feature is defined as the length of the trajectory in the vi-
cinity divided by max(
x
(
t
);
y
(
t
)) (see Fig. 2).
vicinity linearity
: here we use the average squared distance
d²
of each point in
the vicinity to the straight line from the first to the last vicinity point (see Fig. 2).
•
Fig. 3
Pseudo offline features
The features of the second class are all computed using a two-dimensional matrix
B representing the offline version of the data. For each position the number of
points on the trajectory of the strokes is stored. This can be seen as a low-
resolution image of the handwritten data. The following features are used:
•
ascenders/descenders
: these two features count the number of points above the
corpus line (ascenders) and below the baseline (descenders). Only points which
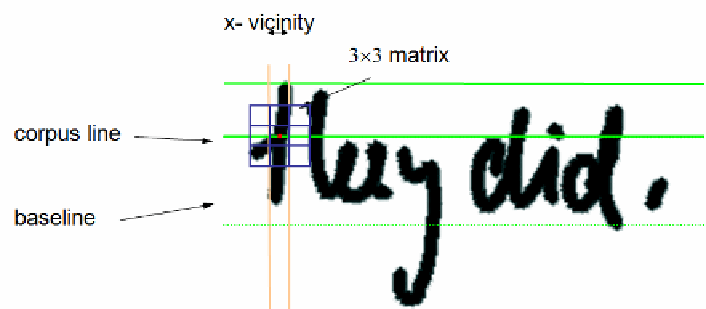
Search WWH ::

Custom Search