Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
methods are presented for automatically or semi-automatically extend the number
of annotated samples,, by using the relatively few manually annotated samples.
In most of the applications and for most types of the input modalities, such as
in audio and visual information, the classification is preceded by a pre-processing
stage of the data. Pre-processing refers to the extraction of processable features
from the raw data. As described in Figure 1.
The definition of the knowledge domain, the collected data and its annotation
influence most of the processing and pre-processing stages of the classification. In
some cases, a second level of abstraction exists between the basic extracted fea-
tures and the classification system or algorithm. Sometimes this level also implies
an intermediate level of abstraction. This involves a group of features that define a
domain of the modality which can be described by itself, and define aspects of the
knowledge domain, such as
rhythm
and
melody
in music analysis [39, 31],
color
and
shape
in computer vision [73], and the like. In other cases, the intermediate
processing stage is required in order to describe spatial and /or temporal properties
of the extracted features. For example, extending the features extracted per-pixel
in images or per-time-frame in audio samples, to patches, segments or regions that
share characteristic values, analysis of the features in these areas, and of the rela-
tions between these areas.
In most cases the number of available features is large, this “dimensionality
curse” may cause over-fitting and extend the classification processing complexity
and time. Many classification processes involve a stage of selection of a reduced
set of features, which are found to be relevant according to the available data.
Sometimes though, different sets of features distinguish different pairs or sets of
classes. In this case, finding a single set of features for distinguishing all the
classes is suboptimal [60].
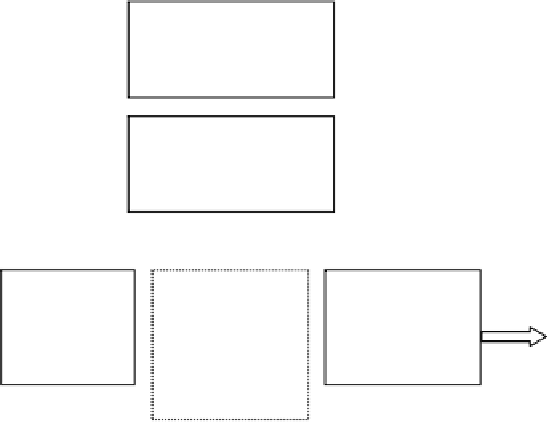
Definition of the
knowledge domain
Data collection
& annotation
High-level
feature
Extraction
Feature
selection
Feature
extraction
Classification
Fig. 1
A schematic description of the classification process




Search WWH ::

Custom Search