Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
7.
Calculate a logical (binary) multiplication of the asymmetry mask
A
and the
brain mask
P
.
8.
Eliminate narrow links between regions. This is done by morphological open-
ing with a semi-circular structural element having the diameter of 3.
9.
The last step of the algorithm is the elimination of all small regions. This is ac-
complished by morphological erosion with a semi - circular structural element
having the diameter of 10. The resultant image is composed of only the regions
that contain some pixels that have “survived” the above operation.
The asymmetry map A is combined with the perfusion map (from step 1 of the
above algorithm). It is very important to notice that above algorithm detects
asymmetry between hemispheres without making decision about its type (ischem-
ic or hemorrhagic) and position of abnormality (which of two hemispheres consist
it).
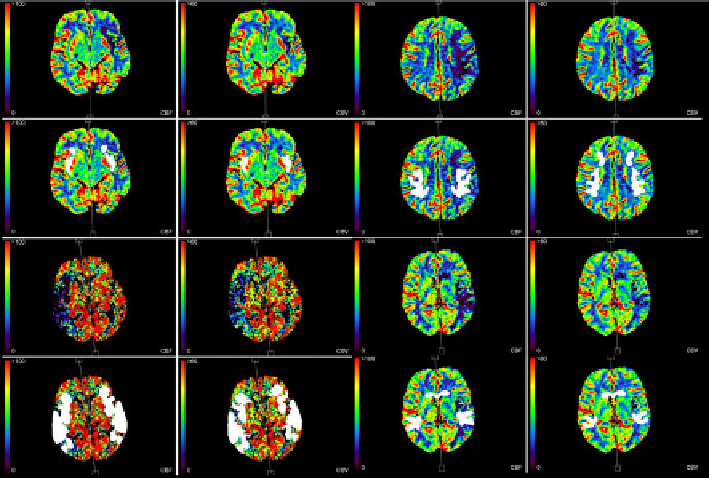
As a result, an asymmetry map is generated in the way shown in Fig 3.
Fig. 3
Four pairs of CBF maps (left in pair) and CBV maps (right in pair). Under each pair
same images with perfusion abnormalities marked as white regions. Asymmetries are
marked in both hemispheres.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search