Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
associated with a high probability of producing infarction [19]. The decreased
CBF and CBV characterize the region with infraction risk. The very low or non-
measurable CBF and CBV means permanent brain cell damages.
3 Image Processing and Abnormality Detection
The medical knowledge about the nature of analyzed data is essential for construc-
tion of proper image - analysis protocol/algorithm. Detection of potential perfusion
lesions in CTP maps is an important part of contemporary brain vascular diseases
diagnosis and treatment planning [22]. The solution proposed by author - perfusion
abnormality detection measure and description (DMD) system [10] [7] is consisted
of a few independents modules (sub - algorithms and knowledge bases):
•
the unified algorithm for detection of asymmetry in CBF and CBV perfusion
maps (proposed in [8], [6]),
•
the image registration algorithm based on adaptation of a free form deformation
model [9],
•
the description / diagnosis algorithm.
System has two knowledge bases: the brain AA (axial CT slices with descriptions -
maps of regions visible in each slice) and the base containing medical information
about average values of brain perfusion. The complete schema of the algorithm is
presented in Fig 2.
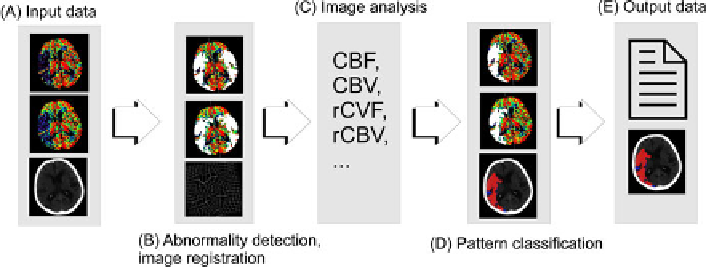
Fig. 2
Schema of DMD system. (A) Input data (CBF, CBV and CT image) is processed (B)
in order to detect abnormal perfusion. System performs image registration with anatomical
brain atlas (brain tissues classification). In image processing step (C) vital perfusion para-
meters (like CBF, CBV, relative CBF and CBV, …) are measured. In pattern classification
step (D) algorithm decides about type of lesions and prognosis for infarcted tissues. Output
data (E) - images and results of classification process are presented to physician.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search