Database Reference
In-Depth Information
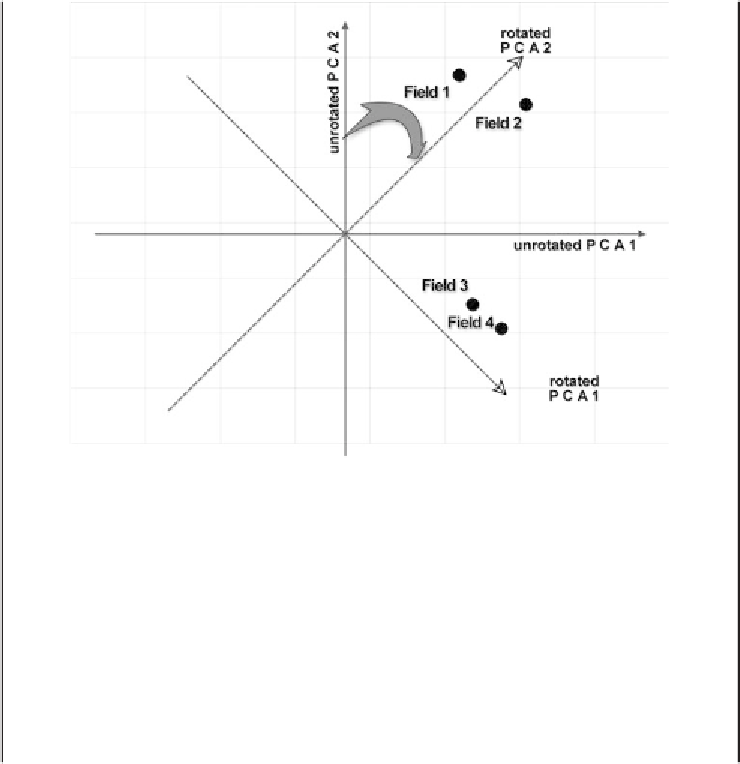
Figure 3.2
An orthogonal rotation of the derived components.
Other rotation methods (like Promax and Oblimin, for instance) are not
constrained to produce uncorrelated components (oblique rotations) and
are mostly used when the main objective is data interpretation instead of
reduction.
Rotation reattributes the percentage of variance explained by each
component in favor of the components extracted last, while the total variance
jointly explained by the derived components remains unchanged.
In Table 3.5, loadings with absolute values below 0.4 have been suppressed
for easier interpretation. Moreover, the original inputs have been sorted according
to their loadings so that fields associated with the same component appear together
as a set. To understand what each component represents we should identify
the original fields with which it is associated, the magnitude, and the direction
of the association. Hence, the interpretation process involves examination of the
loading values and their signs and identification of significant correlations. Typically,
correlations above 0.4 in absolute value are considered to be of practical significance
and denote the original fields which are representative of each component. The
interpretation process ends with the labeling of the derived components with
names that appropriately summarize their meaning.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search