Database Reference
In-Depth Information
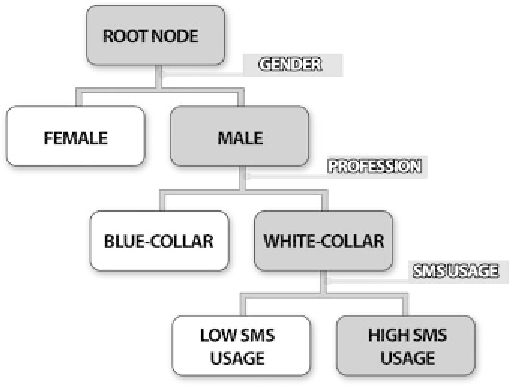
Figure 3.24
An outline of the resulting decision tree model.
Ruleset format. Eventually, the training dataset (root node) is partitioned into
four subgroups (terminal nodes), resulting in four corresponding rules, three
of which classify customers as non-prospective buyers and one as prospective
buyers.
In general, the split-and-grow procedure of a node terminates when:
• All records in a specific node have the same value for the target field, for
instance the node contains only churners, indicating perfect separation and
absolute purity of the node.
• A significant predictor cannot be found and the separation, although not perfect,
cannot be improved further.
• One of the specific user-defined stopping criteria has beenmet. Stopping criteria
are used in order to specify:
- The number of allowed successive splits: users can specify in advance the
maximum tree depth (tree levels below the root) which determines the
maximum number of times the training dataset can be recursively split.
- The number of records of the nodes: users can specify in advance the
minimum number of records of the parent (the nodes to be split) and of the
child (the nodes resulting after partition) nodes.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search