Database Reference
In-Depth Information
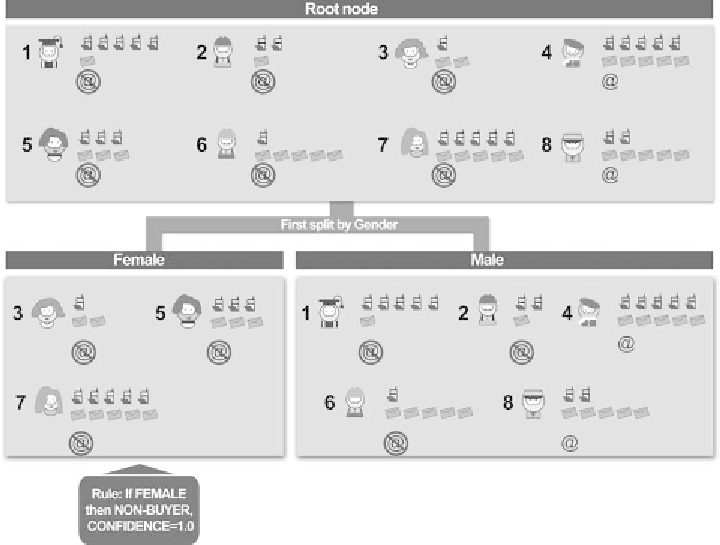
Figure 3.21
First split of the root node in a decision tree model.
To illustrate the tree growth procedure we will revisit the simple cross-
selling example presented in ''Predicting Events with Classification Modeling'' in
Chapter 2. The goal is to use the responses collected from a pilot campaign carried
out on a sample of customers to identify the right prospects for promoting the Inter-
net service. The first step of the decision tree model is presented in Figure 3.21.
Initially, all available inputs are assessed with respect to their predictive ability
and gender is selected as the first split according to the algorithm's criteria. The
entire dataset is partitioned into two subsets (child nodes) according to gender.
Since all women rejected the offer, the ''women'' node is terminal due to perfect
separation and cannot be partitioned any further. Hence the first rule has been
discovered and classifies all women as non-buyers with a respective prediction
confidence of 1.0 and a purchase propensity of 0. On the other side of the tree,
three out of the five men (60%) rejected the offer, thus if the model had stopped at
this level, the prediction would have been no purchase with a respective confidence
of 3/5
0.6. However, there is room for improvement (we also suppose that none
of our stopping criteria have been met) and the algorithm proceeds by further
=
Search WWH ::

Custom Search