Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
STUDY AREA AND AVAILABLE DATA
For the above mentioned reasons, a joint Indo-French Collaborative Project
on groundwater research was launched in 1999 (Ahmed & Ledoux, 1999)
and a number of field investigations were conducted in a watershed in
Maheswaram mandal, about 30 km south of Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh,
India. Some historical data of rainfall, water levels in wells and land-use
were available from the Groundwater Department but much of the field
investigations were jointly performed by the scientists involved in the project.
The studies included the base-line data generation of well inventory,
preparation of geomorphological maps based on aerial photographs and
satellite imageries, geophysical investigations for the delineation of the
extension of weathering in dykes, and across lineaments, mapping of the
weathering profiles, drilling of wells at specific locations for regular
monitoring of water levels, conducting hydraulic tests of short (30 minutes)
duration to mid and long duration (4 to 6 hours, 18 hours), and the monitoring
of a hydrometeorological station. Under the present project, about 25
piezometers have been drilled in the entire watershed to carry out the
hydrological tests and for monitoring water levels and quality parameters.
This considerable but necessary amount of data will form the basis for the
preparation of a model so that future scenarios of water balance could be
established for the management of the limited resource. This paper mainly
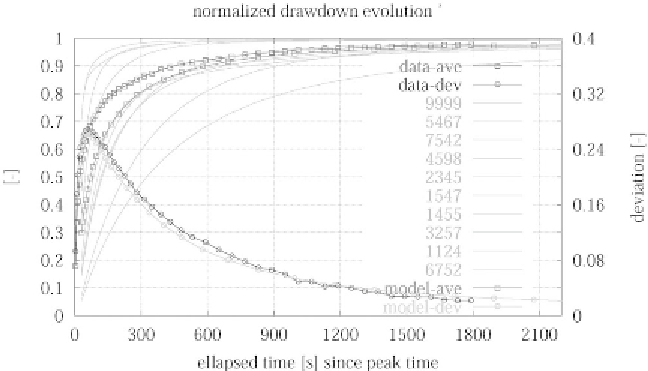
deals with the results of slug tests and the related subjects. Figure 1 shows
the set of normalized slug test responses which will be used later.
Figure 1.
Slug tests responses, normalized versus the initial water level change.
Superimposed is the average value observed at a given time and the standard
deviation measuring the spreading of the responses at that particular time (three
poor responses have been discarded).