Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
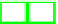
Fig. 3.
Second test environment, using Honeyd and OpenBSD Packet Filter
to the remote machine, are removed or may cause the drop of the packet [10]. If
tra
c normalization is performed on all protocols (IP, TCP, UDP and ICMP)
practically all fingerprinting tools will be affected.
Another problem that affects fingerprint tools is created by the use of SYN
proxies. SYN proxies are one of the widely used techniques to prevent servers
against DoS (Denial of Service) attacks [6]. The SYN+ACK synchronization
message of sent in response to TCP SYN requests are not originated from the
target machine, but instead, from the firewall itself. As result, the use of SYN
proxies also directly affects an identification tool that uses TCP.
Other problem is related to the use of PAT (Port Address Translation) [7,20].
PAT is a technology in which a mapping between the device's port internal
network and the device port exposed to the Internet is made explicitly. The
use of PAT complicates the identification process because the operating system
to be identified depends on which port the tool collects the information. If the
identification tool uses more than one open TCP port to create your fingerprint
this signature will not properly represent the TCP/IP stack of either machine
(remote or the one who perform PAT).
Beyond the use of firewalls there are tools that aim to fool OS fingerprint-
ing [19]. The Honeyd is a tool that aims to simulate machinery, services and
operating systems on the network [17,18]. Therefore, this tool simulates differ-
ent implementations of the TCP/IP stack. In this sense, considering the use of
OpenBSD Packet Filter [2] and the presence of Honeyd, the architecture of Fig. 2
was modified and used as a second test environment, presented in Fig. 3.
This last test environment can reproduce all the security mechanisms intro-
duced in this section. Next section will presents the results for each tool in the
following conditions: (i) in a clean environment, without the use of any security
mechanism; (ii) using PAT; (iii) using packet normalization; (iv) using a SYN
proxy; (v) and using fake machines made with Honeyd.
3 Experiments
In Table 2 are summarized the results of the tests for each analyzed tool, where:
full black circle means correct, half means imprecise and empty means wrong.























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search