Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
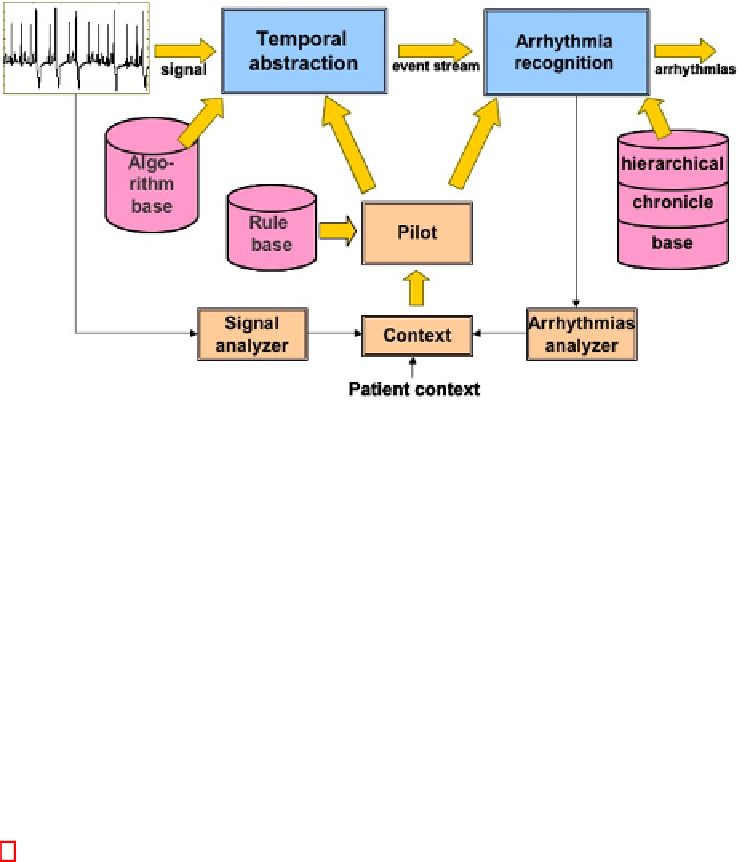
Fig. 3.
The architecture of the online part of the adaptive monitoring system Calicot.
algorithms for detecting their related waves. Thus, low (signal processing) and high
(chronicle recognition) level computations should be tightly coupled. This is why we
opt for an adaptive architecture. On the one hand, a signal processing library containing
many signal processing algorithms was built. Their performance have been assessed
with many noise and disorder parameter values. Then, these values have been clustered
to define abstract contexts that determine when and how to run these algorithms. On
the other hand, a chronicle abstraction hierarchy was defined: more abstract chronicles
contains less event types and/or less event attributes which makes them more relevant
to more noisy contexts. More detailed chronicles are relevant for situations where the
detection of specific events could improve the diagnosis accuracy.
The decisions are taken by a central monitor (that we call a pilot) which analyzes
continuously the signal and the patient context to determine the best signal processing
task and algorithm to execute as well as the related chronicle abstraction level. A cen-
tralized control was adopted because it was simpler to specify via decision rules. Figure
3 gives an overview of the architecture.
5
Temporal Data Abstraction
The temporal abstraction step aims at transforming the numerical series into symbolic
event sequences that are easier to process by high-level diagnosis. In intensive coronary
care units, the main problems come from the presence of different kinds of noise (slow
baseline drift, high frequency noise, impulsive noise) and from the great variability of
patient dependent patterns and which can change over time. For example, multiform
premature ventricular beats (PVC) can combine with permanent or intermittent left or
right bundle branch block. The temporal abstraction level achieves two main tasks:
QRS complex (ventricular activity) and P wave (auricular activity) detection and QRS
classification.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search