Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
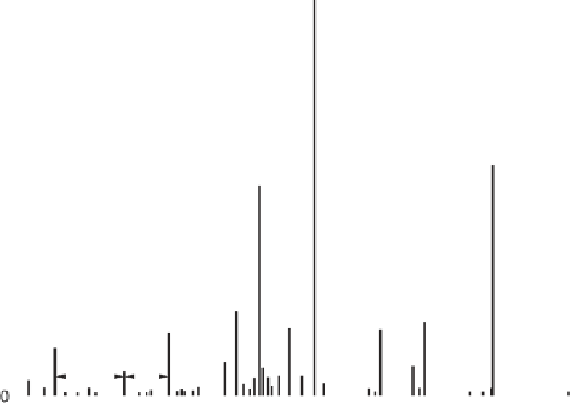
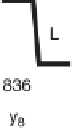
Figure 1.4
Fragmentation spectrum of a peptide is a double fingerprint:
peptide sequence can be read from the amino or carboxy terminus. Fragment
ions (vertical bars) define differences in amino acids masses that make up the
peptide sequence. As an example, a peptide from human cardiac troponin I is
presented. The upper part of the figure summarizes in a mass ladder the
information derived from the MS/MS spectrum. Highlighted on the MS/MS
spectrum are fragment ions showing a difference equal to the molecular weight
of an amino acid.
the number of double bonds) followed by description of the headgroup
[21]. Generally, MS/MS spectra of lipids are less complex than those of
peptides [22]. The presence of ions corresponding to a lipid head group,
easily highlighted in an MS/MS spectrum, together with appropriate
scanning routine is sufficient to profile classes of lipids [23]. However,
lipids identification by MS/MS sometimes requires synthetic analogs





















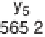

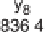
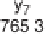
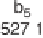






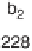

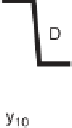




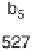


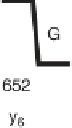


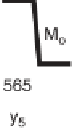

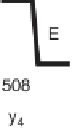

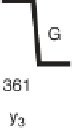



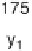

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search