Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
predict a single optimal solution. Methods for enumerating alternative
optimal solutions, and for determining the allowed ranges of fluxes
for optimal solutions, have been developed and applied to genome-
scale models [31-33]. These approaches are especially useful when
flux predictions are compared to experimental data on intracellular or
exchange fluxes.
Sensitivity analysis
. In addition to obtaining an optimal flux distri-
butions or a set of optimal distributions, one may also be interested
in analyzing the effects of changes in parameters of the model on
the optimal solutions (figure 8.3). The simplest question of this type
is how changes in a single maximal reaction rate affect the predicted
growth rate, for example in the case of carbon source uptake [34].
Because of the linear programming structure of problem (5), the
growth rate m is a piecewise linear function of each of the
v
i
max
param-
eters, and the slope of each of the linear regions corresponds to a
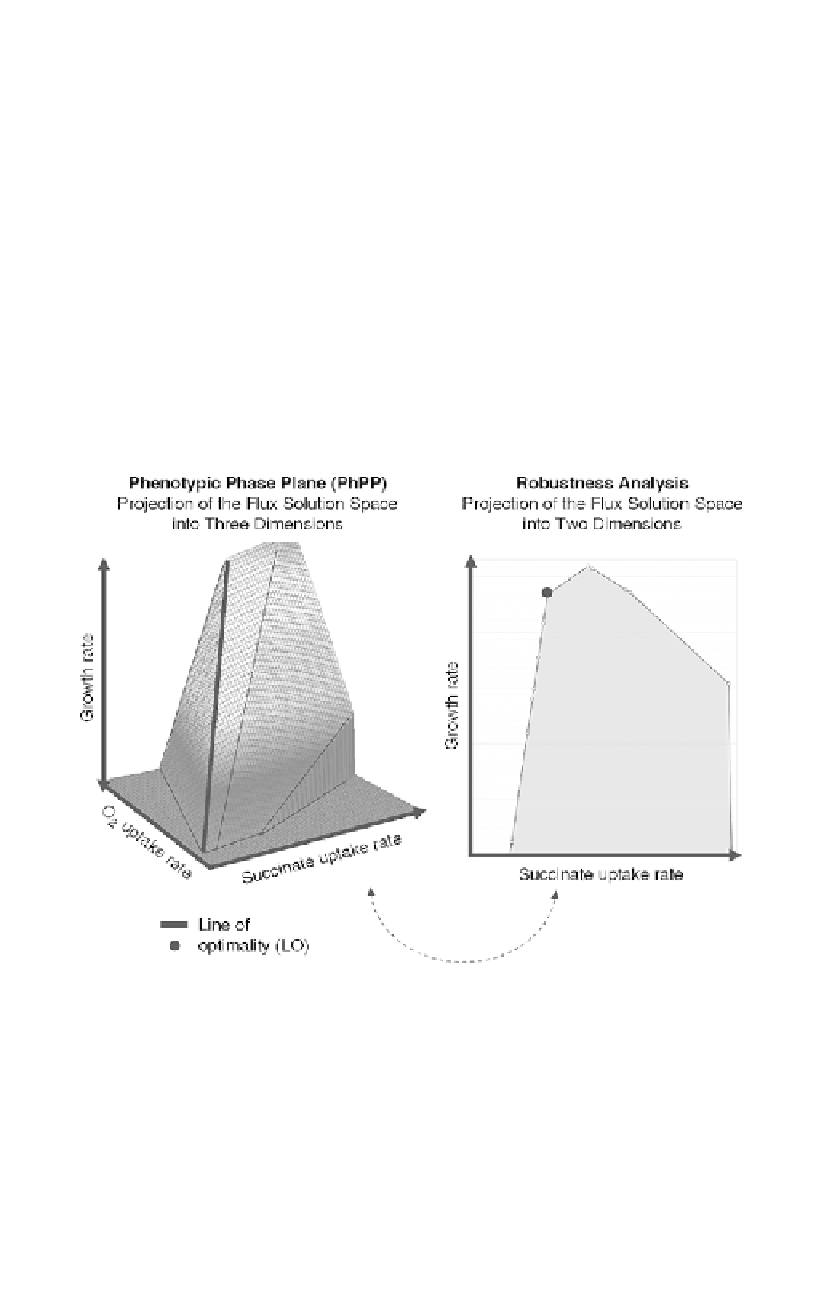
Figure 8.3
Sensitivity analysis of optimal solutions. Phenotype phase plane
analysis allows studying the effects of varying two parameters (here oxygen
and succinate uptake rates) on the predicted optimal growth (or biomass
production) rate. The line of optimality shows the conditions that result in the
optimal biomass yield (biomass production rate/substrate uptake rate).
Robustness analysis of the optimal growth rate to changes in a single
parameter is shown on the right. The point corresponding to the optimal yield
is shown in the graph.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search