Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 4.7
Illustration of the MPSS human breast cancer cell replicate
experiments setup.
coats from five healthy humans, and cultured for about 10 days in
RPMI 1640, supplemented with 20% FBS,
L
-glutamine, 20 mM Hepes,
penicillin, streptomycin, and 50 ng/ml M-CSF, to generate monocyte-
derived macrophages. Macrophages were stimulated with 100 ng/ml
LPS (
S. minnesota
R595 ultrapure lipopolysaccharide, List Laboratories)
and sampled at times 0 h (i.e., before stimulation), 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, and
24 h. For each of these time points, total RNA was isolated with the
Trizol reagent (Invitrogen), the total RNA from the individual donors
was pooled, and poly(A)
+
RNA was isolated with a MicroPoly(A)Pure
TM
kit (Ambion). Culture supernatants were tested to confirm appropriate
induction of cytokines (TNF, IL-6, and IL-12) and an aliquot of total
RNA was tested by real-time PCR to ensure appropriate induction
of selected genes. The poly(A)
+
RNA was processed through the sig-
nature library generation and assayed using MPSS. Duplicate samples
at times 0 h and 4 h were generated using independent cultures of
macrophages and independent pools of RNA for the purpose of replicate
noise modeling.
Results and Analysis
ANALYSIS OF NOISE INHERENT IN MPSS
Following the methods of the above DNA microarray analysis, one
may seek to separate the sources of measurement noise in MPSS by car-
rying out multiple replicate experiments where, at different stages of
the MPSS process, the sample is divided into multiple aliquots and
subsequent steps of the experiments are carried out independently. The
experimental design (shown schematically in figure 4.7) allows one to
separate the measurement variances resulting from signature library









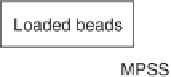

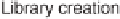


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search