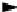Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(4) Gradual evolution is possibly related to uncontinuous phenotype;
(5) Not all the changes of phenotype are the inevitable result of natural selection;
(6) Evolution varies with diversified forms, including changing genes.
(7) Nature selection is based on probability model, not on deterministic model.
d
1
d
2
.
.
.
e
1
e
2
.
.
.
task detector
task subsystem
task effector
learning
subsystem
executive
executive
Fig. 13.1. Execution-oriented learning system
At present, evolutionary computation mainly includes genetic algorithm,
evolutionary strategy and evolutionary programming, which are introduced as
follows.
13.2 Formal Model of Evolution System Theory
Evolution plays its roles in population. Waddington showed the importance of
relationship between genotype and phenotype(Waddinton, 1974). Population rejects
heterogeneous environment. And “epigenetic environment” is a multidimensional
space. The interaction of genotype with environment determines the phenotype,
which then acts through heterogeneously selecting environment. Note that, this
multidimensional space is different from “epigenetic environment”. At this time,
adaptability is the product of phenotype space and selected environment space. It
usually is an one-dimensional function, denoting the contribution of many
offspring to next generation.
Based on the above idea, Muhlenbein and Kindermann presented a model
which was called formal model of evolution system theory(Muhlenbein 1989).
Fig.13.2 shows the relationship of this model. Genotype space(GS) and
phenotype space(PS) are defined by genotype and phenotype, respectively.
GS = {
g
= (
a
…
a
n
)
a
i
Ӥ
A
i
}
(13.1)
1
PS = {
p
= (
p
…
p
m
)
p
i
∈
IR}
(13.2)
1