Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
With the discernibility matrix, we know that the core is {
c
} and the
discernibility function is
c
∧
(
a
∨
d
) or (
a
∧
c
)
∨
(
c
∧
d
). Thus, we can get the two
reducts {
a, c
} and {
c, d
}.
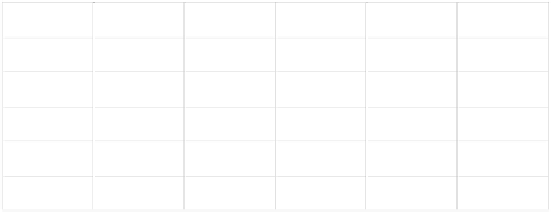
Table 11.2 Discernibility matrix
u
u
1
u
2
u
3
u
4
u
5
u
1
u
2
a, c, d
u
3
a, c, d
u4
a, d
c
a, d
When the number of objects and attributes are huge, the matrix will be very
space-consumed. However, discernibility matrix is intuitionistic, and it can
explain the reduction process. The essence of discernibility matrix based
reduction method is that using the absorption law and other principles in logic
operations to reduce data. Thus, the steps generating discernibility matrixes can
be omitted. Applying the interpretation algorithm of generalized decision logic
formulas, logic formulas related with attributes can be extracted from decision
tables directly. Then the formulas are reduced in logic deduction system. That is,
extract the discernible attributes of objects first (the objects with the same
decision attribute values are not compared) and then generate formulas. At the
same time, he formulas are reduced. At last, the formulas are transformed to
disjunction paradigms, and each element of the disjunction paradigm is a reduct.
The attribute values of u
1
and u
2
, u
3
, u
4
, u
5
are expressed by discernible
conjunction paradigm:
u
5
a, b, c, d
a, b, d
)
With some logic operations like absorption law to get simpler formula
①
:
a
∨
d
(
a
∨
c
∨
d
)∧(
a
∨
d
The attribute values of u
2
, u
3
, u
4
, u
5
are expressed by the addition of
discernible conjunction paradigm and
①
:
(
)
With some logic operations like absorption law to get simpler formula
②
:
(
a
∨
d
)∧(
a
∨
c
∨
d
)∧
c
∧(
a
∨
b
∨
c
∨
d
The attribute values of u
3
, u
4
, u
5
are expressed by the addition of discernible
conjunction paradigm and
②
:
a
∨
d
)∧
c