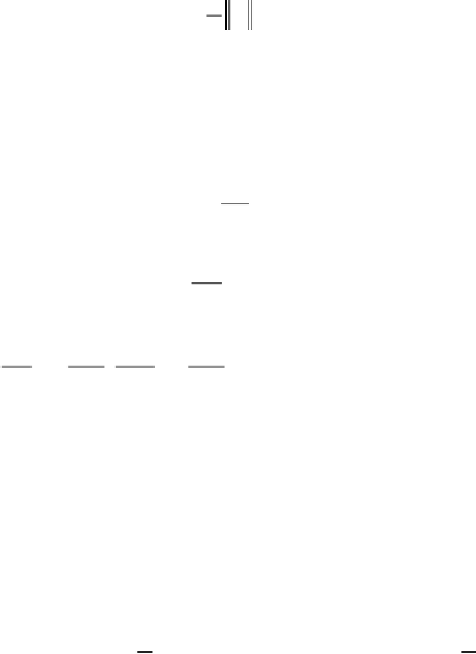Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
optimize function Φ(w) is quadratic form, and the constraint condition is linear.
Thus, it is a typical quadratic programming problem that can be solved by
Lagrange
multiplier
method.
Introduce
Lagrange
multipliers
≥α
0
i
=
1
2
?
,
l
i
1
l
2
Ã
=
L
(
w
,
b
,
α
)
=
w
−
α
{
y
(
x
•
w
+
b
)
−
1
(8.22)
i
i
2
i
1
where, the extremum of
is the saddle point of equality8.22. To find the
saddle point one has to minimize this function over
L
and to maximize it
over the nonnegative Lagrange multipliers α. At the saddle point, the solutions
w
w
and
b
*,
b
*, and α* should satisfy the conditions
∂
Ã
=
L
l
=
y
α
=
0
(8.23)
i
∂
b
i
1
∂
L
l
Ã
=
=
w
−
y
α
x
=
0
i
i
i
∂
w
(8.24)
i
1
∂
Ä
∂
∂
∂
Ô
L
L
L
L
Å
Æ
Õ
Ö
=
,
,
?
where,
.
∂
w
∂
w
∂
w
∂
w
1
2
Therefore, through solving quadratic programming problem, SVM attain
corresponding α* and
w
* satisfying the following equality
l
Ã
=
*
*
w
=
α
y
x
(8.25)
i
i
i
i
1
and the optimal hyperplane (See Figure 8.4).
For transform linearly separable case, the original problem becomes the
following problem.
l
1
l
l
1
Ã
à Ã
max
W
(
α
)
=
α
−
α α
y y x
•
x
=
Γ
•
F
−
Γ
•
A
Γ
(8.26)
i
i
j
i
j
i
j
2
2
α
i
=
1
i
=
1
j
=
1
satisfying the following constraints
l
Ã
=
y
α
=
0
α ≥
0,
i
=
1, 2,
?
,
l
(8.27)
i
i
i
1
ň
=
(
α α
,
,
?
,
α
),
I
=
(1,1,
?
,1)
l
×
l
where,
D
is a
symmetric matrix,
1
2
l
each element is as follow: