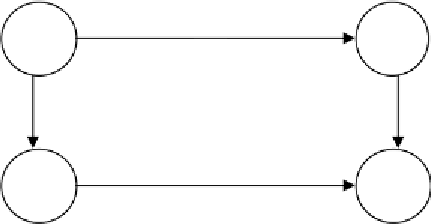Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
problems, an computation model should also have learning skills, I.e., the
skill of adjust the solutions based on past useful experiences. When people
can't obtain the solution to the problem after retrieval and revision to the
existing solutions to similar problems, some weak methods should be
employed. So, analogy learning is a kind of learning based on knowledge (or
experience). The general model of analogical problem solving is shown in
Fig. 5.1.
A
A'
˶
˷
˷Ô
˶Ô
B
B'
Fig. 5.1. The general model of analogical problem
solving
Analogical problem solving can be formulized as: Suppose B is the
solution the problem A, given a new problem A' that is similar to A by some
predefined criteria, how to gent its solution B'? As shown in Fig. 5.1,
represents the dependence between B and A, and is called causality.
is the
similarity of source domain A and the target domain A'.
', the dependence
between B' and A' can be computed on the basis of
and
. The following are
some definitions about analogy learning.
Definition 5.1
(Similarity) Suppose P
1
and P
2
are finite sets of predicates. If q
1
∈
P
1
, and q
2
∈
P
2
are the same, then ordered pair <q
1
,q
2
>
∈
P
1
× P
2
is similar.
Definition 5.2
(Partial Match) Suppose s and t are finite sets of literals with
shared constants. For s
∈
S, t
∈
T, as for Q, if Q
θ
⊆
s
⊆
s × t, and there is an
one-to-one mapping between Q
θ
and
Ȼ
(Q)
θ
, then (Q,
θ
) is a general partial
match of s and t.
Definition 5.3
Suppose (Q,
θ
) and (Q',
θ
') are two partial matches
of s × t. If there is a substitution
ξ
such that Q'
ξ
⊆
Q, and for any W
∈
ν
(Q')
(Intensity)