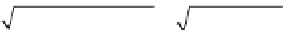Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a reporting period. A geometric mean, unlike an arithmetic mean or average,
dampens the effect of very high or low values that otherwise might cause a
non-representative result.
Note:
Current regulatory requirements prohibit the reporting of no MPN
or colonies. If the test result does not produce any positive results or colo-
nies, it must be reported as <1 (less than 1). In cases where test results are
reported as 0 or <1, a value of 1 should be used to calculate the geometric
mean. This substitution does not affect the result of the calculation; it just
ensures that the data are entered into the calculation in a usable form.
Calculation of the geometric mean can be performed by one of two meth-
ods. Both methods require a calculator capable of performing more advanced
calculations. The first method requires a calculator that is capable of determin-
ing the
n
th root of a number (
n
= the number of values used in the calculation).
The general formula for this method of calculating the geometric mean is
GeometricMean=+++
XX
2
X
n
(6.3)
n
1
This equation states that the geometric mean can be found by multiplying
all of the data points for the given reporting period together and taking the
n
th root of this product.
■
Example 6.3
Problem:
Given the data in the chart below, determine the geometric mean
using the
n
th root method.
Solution:
GeometricMean
=××× =
4
5790
1000
3 150 000
,
,
=
42
c
olonies/100 mL
4
The second method for calculation of the geometric mean requires a calcula-
tor that can compute logarithms (log) and antilogarithms (antilog):
loglog
XXX
+
+ ++
log
3
X
1
2
n
GeometricMeanAntilog
=
(6.4)
n
(numberoftests)
Procedure
1. If there are any reported values of 0, replace them with <1.
2. Using the calculator, determine the logarithm of each test result.
3. Add the logarithms of all of the test results.