Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Ploidy by Cytometry Test - an Alternative Ploidy Test
An alternative method for the cytological root tip chromosome count in ryegrass (
Lolium
spp.) is the
determination of the ploidy level using a low cytometer. The ploidy level (e.g., tetraploid or diploid) in a
sample is determined by measuring the nuclear DNA content of plant cells. The procedure of determining
the ploidy level using the low cytometry method includes: (1) Preparation of nuclei suspension and stain-
ing. Using the proper buffer, nuclear DNA of the plant sample under investigation is prepared and stained
with luorescent dye (e.g., DAPI); (2) Illumination: The stained materials are exposed to special light inside
the low cytometer where the stained nuclear DNA will luoresce; and (3) Determination of ploidy level:
Ploidy level is determined by measuring the luorescence light intensity emitted from stained molecules of
a particular sample. This emitted light is proportional to the chromosomal DNA content of that sample. The
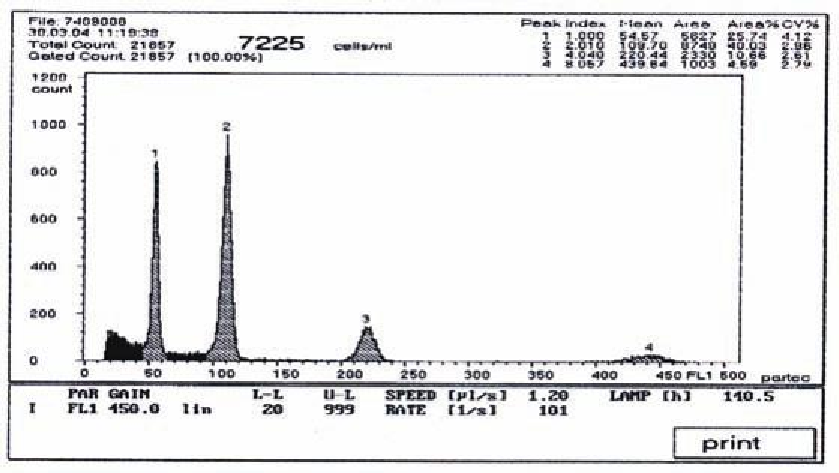
low cytometer plots the results in a histogram (Fig. 9.16). An internal check sample is used to compare the
peak of DNA content of the test sample to that of a known check sample.
Figure 9.16. Histogram demonstrates the relative luorescence of stained nuclear DNA of diploid ryegrass
(channel 54 on the x-axis) and tetraploid ryegrass (channel 109 on the x-axis) using the low cytometer.
GroWTH CHAMbEr TESTInG
Growth chamber testing involves growing and evaluating seedlings and plants in a controlled, uniform envi-
ronment. This insures that all seedlings and plants are grown under the same conditions and that observed
differences have a genetic basis. The AOSA Cultivar Purity Testing Handbook cites two basic approaches
to growth chamber testing. One involves growing plants under conditions that accelerate growth, and the
other involves growing plants under one or more environmental stress conditions for evaluation of spe-
ciic cultivar responses. The choice of approach depends on the plant characters being tested, keeping in
mind that quantitative characters are highly inluenced by environmental conditions. Regardless of testing
procedure, appropriate reference samples should be tested along with the test sample to ensure that results
obtained are true varietal differences rather than artifacts of the testing procedure.