Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Test for oats (
Avena sativa
L.)
The HCl test for oat seeds is useful for testing treated or weathered seeds when the results of the luores-
cence test are in doubt.
Procedure
1. Place oat seeds in a glass beaker and cover with a solution consisting of one part concentrated
(38%) hydrochloric acid (HCl) and four parts distilled water for 6 h.
2. After the 6 h soak, remove the seeds from the HCl solution and air dry (about 1 h) on white ilter
paper.
3. Classify the seeds as tan (luorescent) or yellow (nonluorescent).
Peroxidase Test for Soybean (
Glycine max
[L.] Merrill)
Buttery and Buzzell (1968) were able to separate soybean varieties into two groups based on the presence
of either high or low seed coat peroxidase activity. Payne (1986) reported that neither seed quality nor seed
storage conditions affected the results of this test. The test is currently listed by AOSA Rules for identiica-
tion and cultivar determination of soybeans (AOSA Rules, Section 2b.2).
Procedure
1. Remove the seed coat from a soybean seed and place into a test tube or suitable container.
2. Add 10 drops of 0.5% guaiacol to the test tube.
3. After 10 min, add a drop of 0.5% hydrogen peroxide.
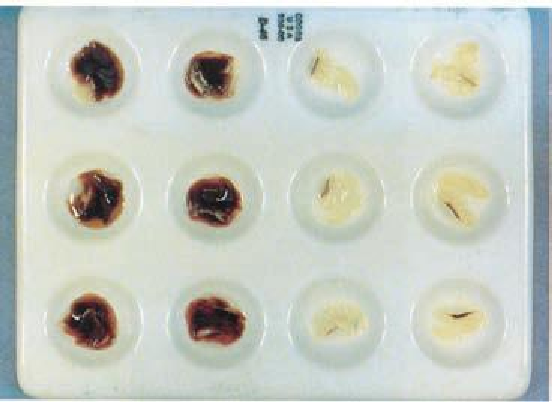
4. One min after adding the hydrogen peroxide, record the seed coat as peroxidase positive (high
peroxidase activity) indicated by a reddish brown solution or peroxidase negative (low peroxidase
activity) indicated by a colorless solution in the test tube (Fig. 9.10).
Figure 9.10. The peroxidase test for soybean: Peroxidase positive (left two rows), peroxidase negative (right
two rows).