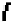Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Hi
gh lateral margin
influence
σ
n
on rupture
surface, usually following
clay/marl/s
hal
e layer.
Very high
α
av
α
≈ φ
r
Large Rock Glide
Rupture surface follows stress relief
cracking or joints
La
rge difference between peak and
residual friction angles.
α
av
α
≈ φ
r
Dominant rock mass
anisotropy dips into
slope
Rough Translational Slide
Planar bedding or
major structures
α
av
α
av
≈ φ
r
Planar Translational Slide
α
av
> φ
r
'
Localised buckling failure of
str
at
a at toe
α
av
Toe Buckling Translational Slide
Figure 2.44.
Summary of features of large rapid rock landslides - Sheet 1 of 2 (Glastonbury 2002,
Glastonbury & Fell 2002c).