Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 19.46.
Factors involved in estimating infiltration through cover over tailings.
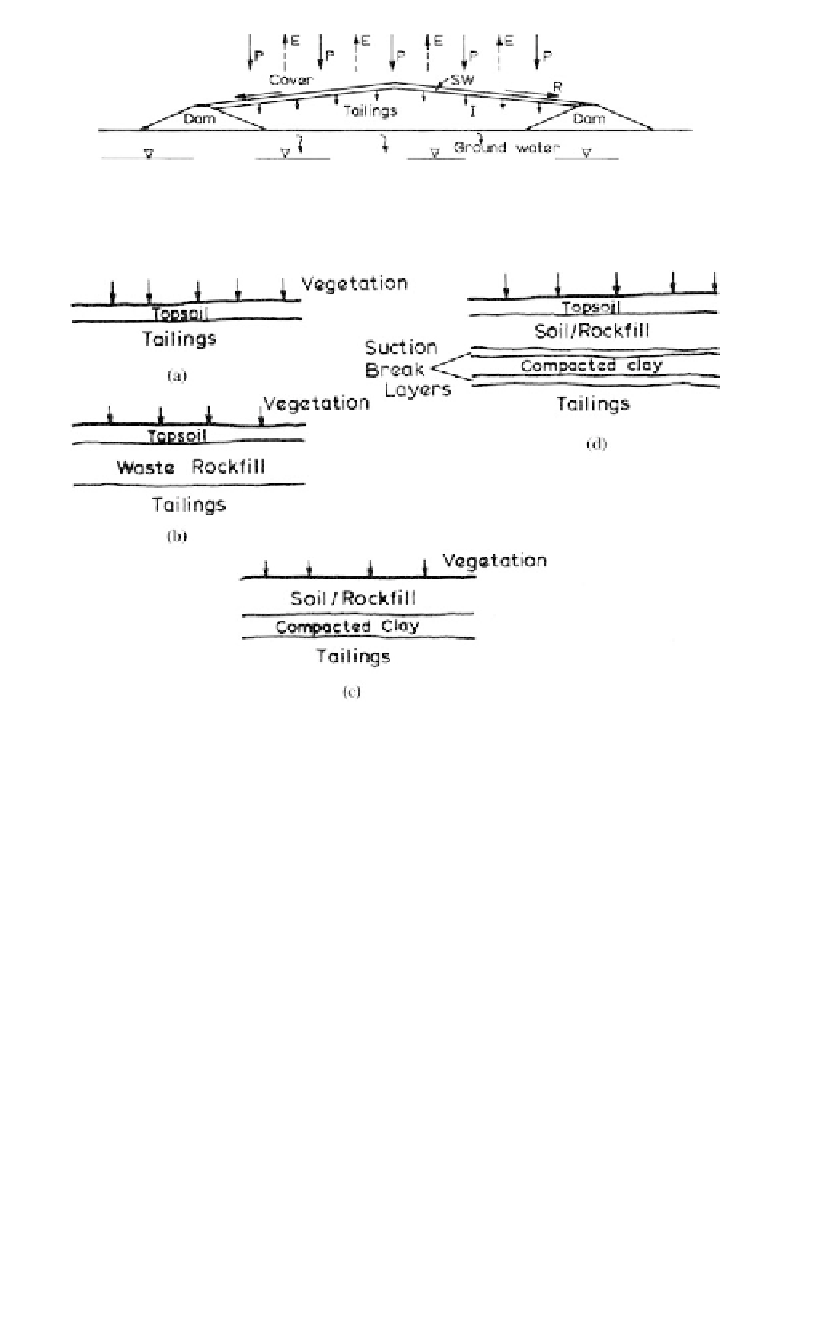
Figure 19.47.
Some alternatives for covering tailings.
In these figures:
- The vegetation controls erosion, promotes evapotranspiration and enhances the
appearance and use of an area;
-Topsoil promotes the vegetation. Note that in some cases vegetation can be established
directly on to tailings;
- Soil rockfill is to control erosion and protect the underlying compacted clay from desicca-
tion (in (d)).
- Compacted clay is a “barrier” to infiltration (in reality it only reduces infiltration since
it will have a finite permeability);
- Filter layers are to prevent migration of fines into the drainage layer (a);
- Suction break layers are sand layers which assist in controlling desiccation and hence
cracking of the compacted clay and help prevent transfer of salts and contaminants up
through the compacted clay from the tailings.
The adopted design will depend on environmental constraints and availability of mate-
rials. Geotextiles and geomembranes may also be used, but are not common for tailings
or waste rock dumps because they are too expensive for the large areas involved.
Accurate estimation of the rate of infiltration through the cover is difficult (almost
impossible).