Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
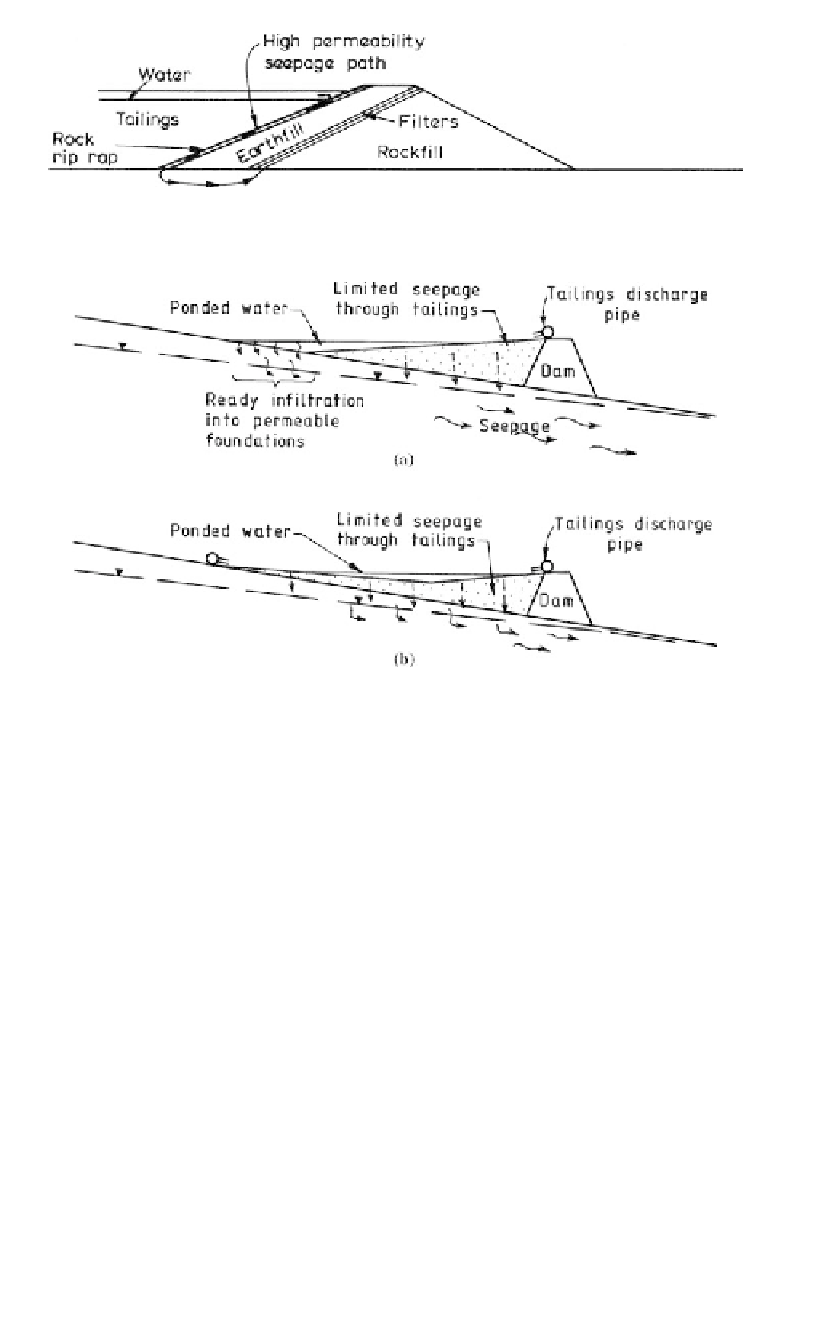
Figure 19.40.
Seepage through rock rip-rap bypasses low permeability tailings.
Figure 19.41.
Controlled placement of tailings: (a) tailings not covering foundation; (b) tailings cover-
ing foundation.
- Failure to allow for preferred seepage paths, e.g. high permeability, jointed or
closely jointed zones;
- Failure to consider adsorption, dispersion etc.
19.6.4
Seepage control measures
Measures to control seepage from tailings storages include:
- controlled placement of the tailings;
- foundation grouting;
- foundation cutoffs;
- clay liners;
- underdrains and toe drains.
19.6.4.1
Controlled placement of tailings
In many cases, the most cost effective way of controlling seepage will be to place the tail-
ings so that the base of the storage is blanketed. Figure 19.41 shows this effect with the
tailings forming an effective blanket in (b) but not in (a) where water is in direct contact
with the foundation.
In theory, provided the tailings are of low permeability, they will form as effective a liner
to the storage as can be achieved by a compacted clay liner. Vick (1983), for example,