Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
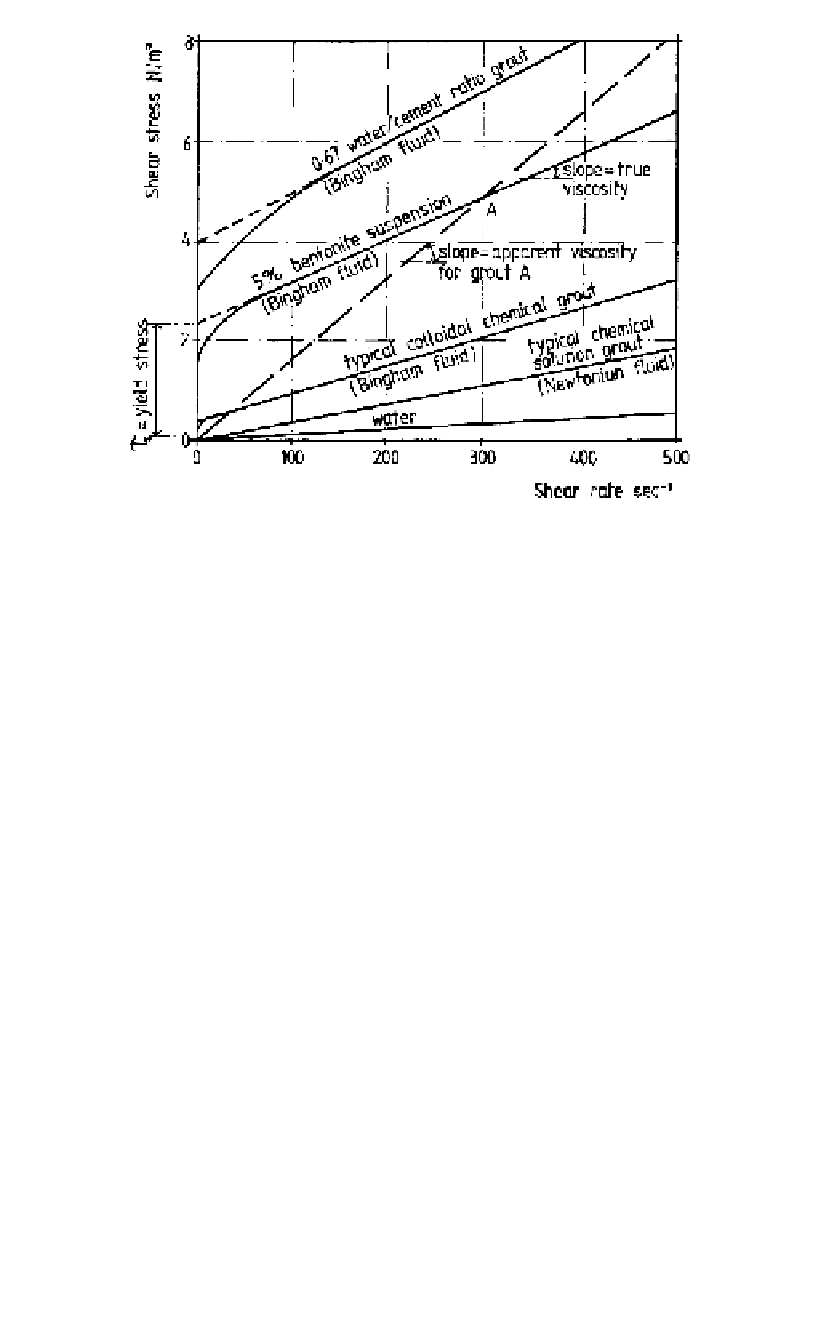
Figure 18.23.
Typical flow properties for grouts (adapted from Littlejohn, 1985).
the line passing through the point (e.g. Point A) and the zero point (rather like a secant
modulus compared to a tangent modulus for true viscosity). The intercept of the curve on
the shear stress axis is the “yield stress” or “yield value” (also called “cohesion” by
Lombardi, 1985, by analogy with the shear strengths of soils). The value quoted will
depend on the shear rate and may be determined by extrapolation of the straight line por-
tion of the curve as shown in Figure 18.23.
Most methods of measuring will give the apparent viscosity, rather than the yield stress
and true viscosity and this must be taken into account. The authors' experience is that,
with cement grouts, the method proposed by Nguyen and Bogor (1983, 1985) which uses
a very sensitive vane shear type apparatus is the most successful.
The viscosity is dependent on the concentration of the grout and the time after mixing.
Figures 18.24
and
18.25
show these effects.
The gel time is dependent on time and temperature and on additives which are deliber-
ately used to control it. This is discussed in Littlejohn (1985) and Karol (1985).
There are many types of grout available and new products are coming onto the market
all the time.
Tables 18.5
and
18.6
list some of the more common grouts and their proper-
ties. Karol (1982a, b, 1983) and Littlejohn (1985) discuss chemical properties of grouts in
more detail.
18.4.2
Grout penetrability in soil and rock
Grout penetration is dependent upon:
(i) Whether penetration is by permeation (impregnation) in the voids in the soil or by
causing hydraulic fracture by exceeding the
in situ
horizontal stresses (0.5-2 times over-
burden pressure), or a combination of both. Australian and general overseas (except
French) practice is to limit pressures to the permeation phase;
(ii) The viscosity properties of the grout and then the pressure and time for which grout-
ing proceeds.