Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
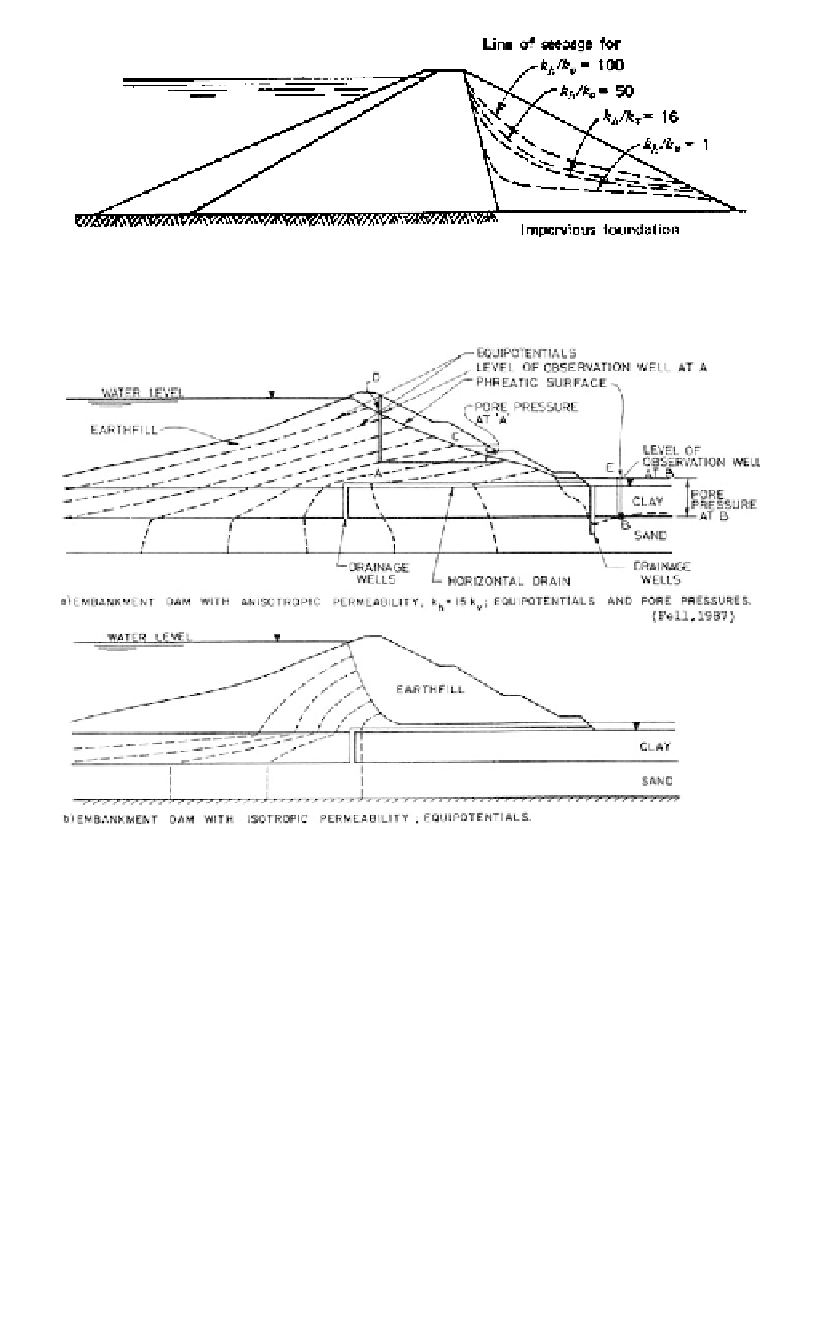
Figure 11.12.
Effect of k
H
on pore pressures in a zoned earthfill embankment (Cedergren, 1972.
Reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons Inc.).
Figure 11.13.
Effect of foundation permeability on seepage flownet at Mardi Dam (PWD of NSW,
1985; Walker and Mohen, 1987).
be affected by fissures, root holes or layering during deposition) will almost invariably
have a permeability far greater than compacted earthfill e.g. in the range 10
5
to
10
6
m/sec. Figure 11.13 shows the effect of such permeability contrasts on the seep-
age flownet for a earthfill embankment with a horizontal drain (Mardi Dam).
The following further points are made on Mardi Dam:
(i) Figure 11.13 shows the calculated seepage equipotentials for k
H
/k
V
15 in the
embankment. These give pore pressures compatible with those observed in the
embankment;
(ii) For both cases (a) and (b) most seepage from the reservoir is through the foundation
- equipotentials in the embankment upstream of the centreline are nearer horizontal
than vertical;
(iii) Even though k
H
/k
V
for the dam was
15 and seepage was emerging on the down-
stream face of the embankment, flow in the downstream part of the dam was
towards the horizontal drain, yielding relatively low pore pressures. However the
drain capacity was exceeded, so pore pressures built up in it.