Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 10.1.
Ben Lomond project - rock mass permeabilities (Coffey Partners, 1982).
10
7
)
Depth to base of zone (m)
Permeability (m/sec
Zone
Avg.
Avg.
Range
Weathered rock with clay infilled joints
0-12 (8)
1.5
0.1-54
Weathered rock (limonite
19-27 (22)
8.0
0.1-27
stained and coated joints)
Rock in stress relief zones
20-36 (28)
108.0
4.8-
200
Average rock mass zone (fresh rock)
-
2.6
0.1-10
Sandstone bed - Unit 3 -
75
Folded zone (western end of site)
-
43
0.5-
200
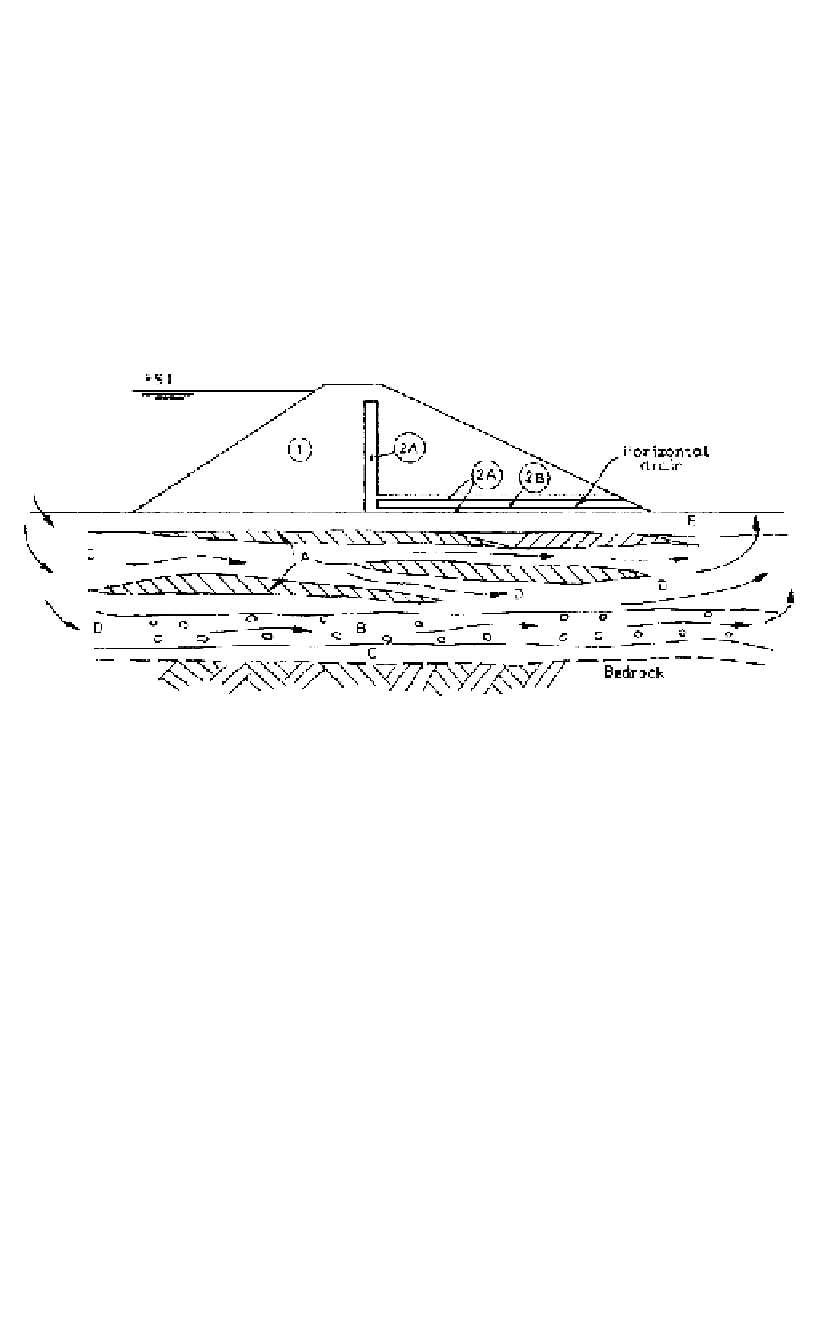
Figure 10.2.
Some common features of alluvial foundations.
Some rocks, such as basalt, inter-bedded sandstone and shale with stress relief
joints, limestone and granite with stress relief effects, are particularly susceptible to
having open joints. If these rocks are exposed in the cutoff foundation, the core mate-
rial may erode into the joints. If the rock around the joints is completely weathered it
may erode into the open joints under seepage from the reservoir.
(b)
Alluvial soils.
Some features of alluvial foundations are shown schematically in Figure
10.2. They include:
A: Lenses or layers of lower permeability sand, silty sand, or even clayey sand may
occur, giving a very much reduced vertical permeability. These may be present in
point bar deposits;
B: There is often a coarser gravel, or even boulder/gravel layer at the base of the allu-
vium (channel lag deposit), reflecting the time when the river was more active. This
may be very permeable;
C: The upper part of the rock surface may be permeable because of the presence of
open joints, potholing and destressing. The surface may also be very irregular;
D: The coarse alluvium - sand/gravel is in itself likely to be layered giving a high per-
meability ratio k
H
/k
V
, e.g. point bar deposits;
E: There is often a layer of silty sand/silty sandy gravel on the surface, giving a low per-
meability, e.g. in flood plain deposits.
In general these features combine to give a much greater horizontal than vertical
permeability. Hence while water can enter into the foundation in the large area of