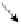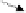Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4
N
1
N
2
4
2A
P
Drawdown
seepage
condition
3
P
1
2A
2B
N
2
3
2C
N
1
2D
N
1
N
1
Sandy grave
l
S
il
t
y
san
d
2A
P
N
1
N
1
Sandy gravel
Rock
LEGEND
Zone
Description
Earthfill
Filter/drains
Earth or rockfill
Rip rap
1
2A
2B 2C 2D
3
4
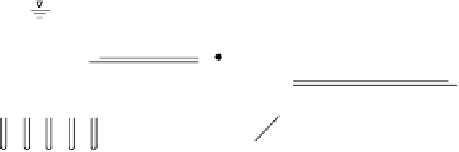
Figure 9.1.
Flow conditions acting on filters. P
flow parallel to interface; N
1
flow normal
to interface, high gradient conditions; N
2
flow normal to interface, low gradient conditions.
a
b
d
d
Reservoir
c
e
e
i
g
Drainage layers
f
Rip rap
Fill
Core
Fill
f
g
d
d
h
g
internal erosion under N
1
flow conditions.
Figure 9.2.
Filter functions (adapted from ICOLD, 1986).
As will be described in Section 9.2, the erosive stresses are greatest for case N
1
, and less
for N
2
because for N
2
the flow is draining from the base soil under gravity, not under
reservoir water head.
The erosive action for case P is different and also less severe than for N
1
. As a result less
conservative (and therefore coarser) filter may be used for cases N
2
and P than for N
1
.
9.1.3
Critical and non critical filters
Figure 9.2 and
Table 9.1
show a number of applications of filters in dams. Some filters are
critical to the control of internal erosion in the dam and, if they fail, give an increased like-
lihood of piping progressing and potentially breaching the dam. These are termed critical
filters, and they should be designed and constructed to meet stringent, no-erosion filter cri-
teria. Examples are filters “g” in Figure 9.2. Some filters are non-critical, in that, if some
erosion occurs, it can be repaired (e.g. beneath rip-rap, locations “a”, “b” and “c” in
Figure 9.2) or it will cause problems only during construction (“d” and “e”, in Figure 9.2).
Most critical filters are in an N
1
flow condition (Section 9.1.2) and non-critical filters
in an N
2
or P flow condition.
Filters “f” and “h” are critical to the performance of the dam, but are in N
2
flow con-
ditions, so may be designed and constructed to lesser standards. Filters “d” and “I” may be
critical or non-critical, depending on whether or not erosion of the embankment fill into