Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 1.2.
Embankment dam foundation treatment.
Item
Description
General foundation excavation
Excavation of compressible and low strength soil and weathered rock
as is necessary to form a surface sufficiently strong to support the
dam and to limit settlement to acceptable values
Cutoff foundation excavation
Excavation below general foundation level to remove highly
permeable and/or erodible soil and rock
Curtain grouting
Drilling of holes into the foundation and injecting grout (usually
cement slurry) under pressure to reduce the permeability of the rock
Consolidation grouting
Grouting carried out in the upper part of the cut-off foundation to
(also called “blanket grouting”)
reduce permeability (of the rock)
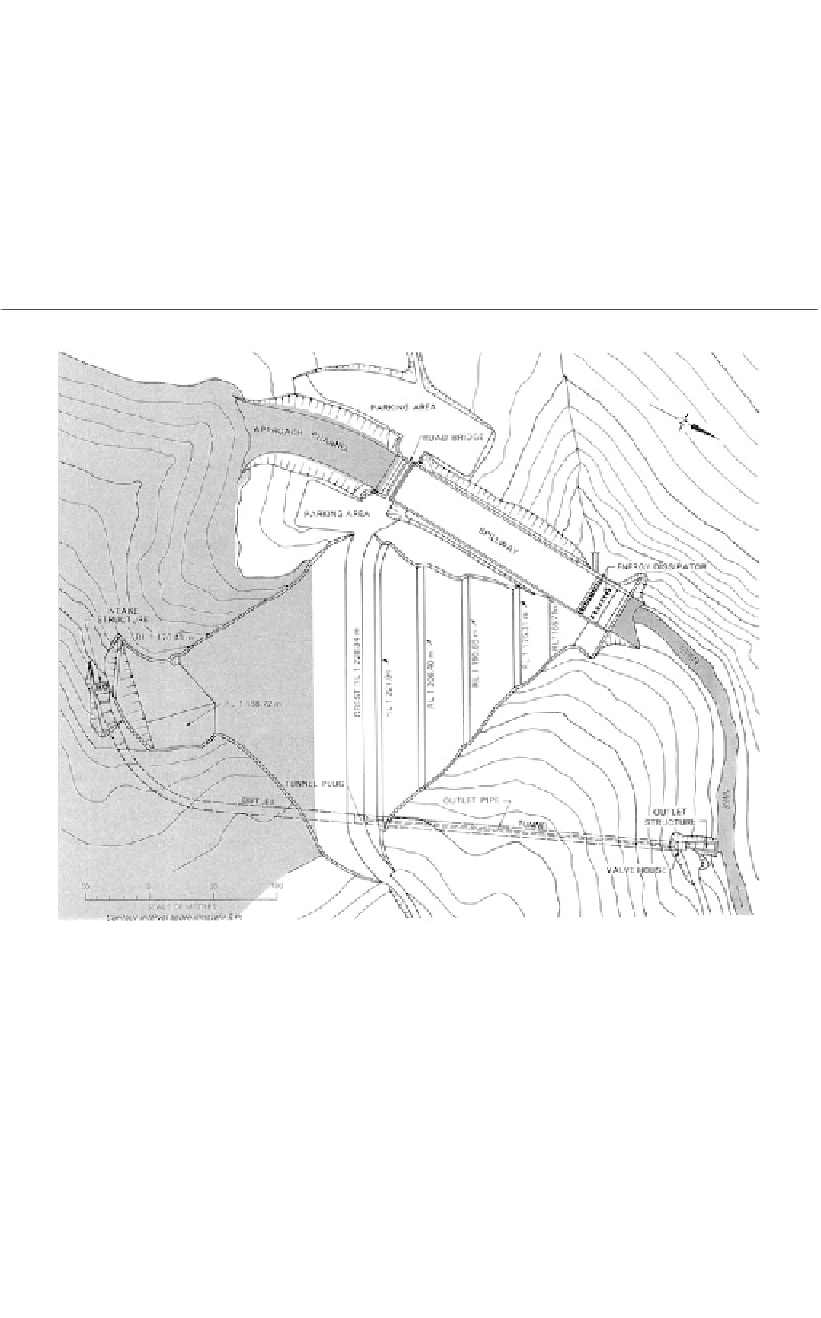
Figure 1.4.
Plan of typical embankment dam and associated structures.
no longer being built. There are other types of embankment dams, but these are not specif-
ically covered in this topic including:
- Concrete face earthfill;
- Asphaltic core rockfill;
-Bituminous concrete face earth and rockfill;
-Steel face rockfill;
-
Geomembrane face earth and rockfill.
Table 1.2 describes the foundation treatment commonly used in embankment dams.
Figure 1.4 shows a fairly typical plan of an embankment dam showing the spillway, out-
let tunnel (which is commonly used for river diversion during construction of the dam) and
outlet structures.