Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
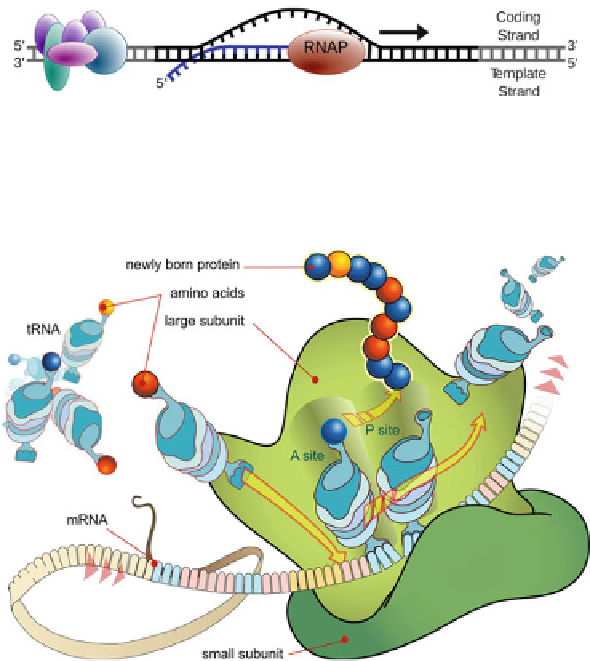
Fig. 2.1
Gene transcription (steps (3) and (4) in the Introduction): the enzyme RNA polymerase
(RNAP) binds to DNA (
black
double strand) and produces a strand of RNA messenger (
blue
strand). This blue strand is a complementary copy of a sequence of DNA code (Image taken
from [
2
])
Fig. 2.2
Translation and protein synthesis (step (5) in the Introduction): a ribosome (two
green
units) is a large complex involving specific RNA (ribosomic RNA) complexed with proteins,
synthesizing a polypeptide chain from a messenger RNA. Such a chain may form a protein on
its own, or may contribute to a multimeric protein, see also Chap. 1 (Image taken from [
1
])
protein (see Fig.
2.2
). Transcription factors are particular proteins that can recognize
DNA motifs on the genome and consequently stimulate the transcription of a precise
gene. A recognition motif is a short DNA sequence that is specific to a certain
transcription factor. The transcription factor itself can be considered as a sensor
of the cellular context.
2.1.1
Biological Systems and Experimental Techniques
A first example is provided by the Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1), which
is stimulated when oxygen pressure decreases: chemically, low intracellular oxy-
gen concentration impairs the hydroxylation of the HIF-1
α
subunit, which leads
Search WWH ::

Custom Search