Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
i
A
i
C
i
B
P
3
[
λ
]
P
3
[
λ
]
P
3
[
λ
]
P
2
[
λ
]
P
1
[
λ
]
P
1
[
λ
]
P
2
[
λ
]
P
1
[
λ
]
P
2
[
λ
]
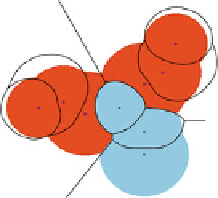
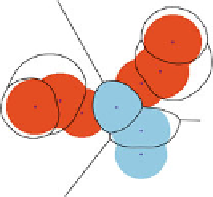
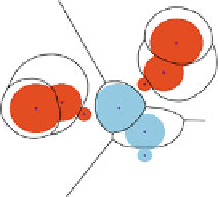
Fig. 1.11
Tracking the interactions of
th
e three toleranced proteins of Fig.
1.9
. The sub-figures
(
a
,
b
,
c
) respectively show grown balls
B
i
[
λ
]
for
λ
=0
,
0
.
5
,
1
. The region of the plane consisting
of points first reached by a growing toleranced ball is the Voronoı region of this ball, represented
by
solid lines
. Colored solid regions feature the
restrictions
—each an intersection of a growing
ball and its Voronoı region. Along the growth process, the restrictions intersect in three points
i
A
,i
B
,i
C
, represented as
blue squares
P
1
P
3
λ
P
3
λ
=1
i
C
:
λ
C
∼ .
9
P
1
P
2
P
3
i
B
:
λ
B
∼ .
4
P
1
P
2
i
A
:
λ
A
∼ .
1
P
1
P
2
λ
=0
Skeleton graphs
P
1
P
2
P
3
Fig. 1.12
Hasse diagrams encoding the interactions of the three toleranced proteins of Fig.
1.9
.
Black tree
: all instances;
red tree
: red instances only
of a complex
C
. For example, at
λ
=
λ
b
(
C
), the complex gets formed by a merge
of two or more complexes; at
λ
=
λ
d
(
C
), the complex dies by merging with at least
another complex. Thus, the
lifetime
s
(
C
)=
λ
d
(
C
)
− λ
b
(
C
) provides a measure
of the topological stability of the complex
C
. Also, the
ancestors
and
successors
of
C
are the complexes contained in and containing, respectively, the complex
C
.See
Fig.
1.12
for an illustration.
In the bicolor setting, let
T
be the list of red protein types. A complex
C
of
the Hasse diagram is made of instances whose types are in
T
. If each type of
T
is
present exactly once in
C
,thecomplex
C
is termed an
isolated copy
. The number
and the lifetime of isolated copies give a measure of the separability of the different
copies of a complex involving all the types of
T
. Note that the intersection of the
lifetime intervals of the different isolated copies may be empty.
We note in passing that we track the evolution of connected components, but not
that of higher order homology generators. In fact, the investigation of the stability of
topological features, for collection of balls and more generally for nested topological
spaces, falls in the realm of
topological persistence
[
25
].














































Search WWH ::

Custom Search