Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
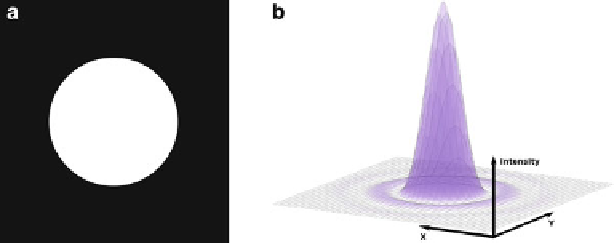
Fig. 4.4
(
a
) A diffracting aperture represented here as a uniform disc (Courtesy Inria), and (
b
)the
2-D Airy disk pattern after diffraction by the aperture (Adapted from Wikimedia Commons)
small circular aperture (Fig.
4.4
a), such as an objective lens in a microscope, it does
not produce a bright dot as a 2-D image, but rather a diffused circular disk, known
as Airy disk, surrounded by much fainter concentric circular rings (Fig.
4.4
b). This
Airy disk is the system's response to an impulse (here a Dirac source) signal and
it constitutes the best description of the imaging properties of the optical system
(here a microscope) [
10
]. This non-random spreading of a point light source, or
blurring, is a consequence of diffraction by a limited aperture (either the objective
or the condenser lens or both). An image whose resolution is thus constrained is
said to be “diffraction-limited” [
32
]. The experimental measurement of this barrier
by Abbe (Eq.
4.1
), which was discussed in Sect.
4.1
, is exactly due to diffraction.
Effect of Pinhole Size.
The size of the pinhole in a CLSM is calibrated against the
diffraction rings. The sizes of the pinholes are annotated by their back-projected
4
values in Airy units (AU). We define 1 AU=(1
.
22
λ
ex
)
/
NA,where
λ
ex
is the
excitation wavelength. As we reduce the pinhole size, the diffraction rings are
blocked out. At 1 AU, the pinhole has about the size of the central principal
maximum. From our experiments in [
52
], with a sample from the
Arabidopsis
thaliana
plant immersed in water, it was observed that, with sizes
<
1 AU there
might be more contrast and less blur, but there are very few photons detected at the
PMT. This is on top of the low Quantum efficiency (QE)
5
of the PMTs (around 6 %).
While, images obtained with pinhole sizes
>
3 AU have larger spot and more intense
signal (signal from the region of interest and out-of-focus signal), but loss in contrast
as well due to unwanted fluorescence. As far as the photon statistics are concerned,
one could even say that the microscope almost behaves like a wide-field because of
4
Back-projected diameter is the diameter of a pinhole in the object space. It is equal to the ratio
between the real physical diameter of the pinhole and the total magnification of the system.
5
Quantum efficiency for a photosensitive device measures the percentage of photons hitting the
photoreactive surface that will produce an electron-hole pair. It is an accurate measurement of the
device's electrical sensitivity to light.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search