Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
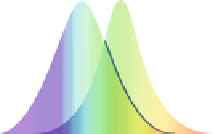
a
b
Fig. 4.1
(
a
) Jablonski diagram of a fluorescent event.
S
0
is the ground state or the steady state
of the fluorescent molecule and the molecule is excited to the singlet state
S
2
by absorbing the
energy
E
in a specific wavelength. The molecule undergoes some internal conversion or vibrational
relaxation and transits to the relaxed state
S
1
by releasing some of the energy. The molecule finally
returns to its ground state by releasing the remaining energy as fluorescence. (
b
) The excitation
and emission spectra showing the Stokes shift towards the
red
light (Adapted from Wikimedia
Commons)
to the excitation intensities. Fluorescence microscopes are equipped with a set
of filter block, each consisting of an excitation filter, a dichroic mirror and an
emission filter. The excitation filter, as the name implies, is inserted along the
path of the illumination light so that an excitation beam of the desired wavelength
can be chosen. On the other hand, the emission filter is designed to permit only
the emitted light generated by the fluorescent objects, and to proceed to the
detector (Fig.
4.2
a). Photons emitted from the fluorescent sample are collected
by a photon sensing device (a PMT or the Charge coupled device (CCD) of a
camera). The contrast obtained by this kind of optical method is far superior than
classical transmission microscopy methods that are based on light absorption by
counter-stained specimens. Two dimensional fluorescence micrographs can then
be reconstructed, to form a 3-D representation, by computationally combining the
image data from a stack of images.
For the sake of completeness, we should mention, very briefly, a number of
fluorescent microscopes that have been more recently developed and commercial-
ized to overcome the diffraction barrier described in Sect.
4.1
.Thesefar-field
1
super-resolution techniques include Stimulated emission depletion (STED) , Photon
activated light microscope (PALM) (and similar), and the Structured-illumination
microscope (SIM). PALM, is based on the principle of photo-activation of a
very small fraction of switchable fluorophores.
2
First a small fraction of the
1
The near field (or near-field), far field (or far-field), and the transition zone are regions of the
electromagnetic radiation field scattering off an object. Certain characteristics of electromagnetic
fields dominate at a large distance (or zone) from the scattering object, while a different
characteristic can dominate at a shorter distance.
2
Molecules having two states, one fluorescent and the other non-fluorescent, and the ability to be
switched from one state to the other by excitation with a shortwave light.




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search