Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
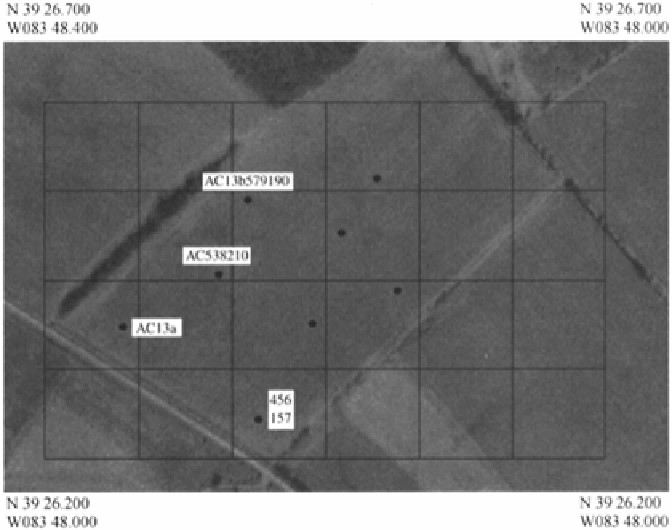
FIGURE 5.3
Sampling grid placed on an aerial photograph showing sample
locations and numbers.
be obtained. A detailed description and discussion of the whole field of navigation, data,
UTM, and UTC will not be covered here; however, an excellent resource covering these
topics is given in Ref. [2].
Global positioning system instruments range from inexpensive handheld units with
limited capacities to stationary units with multiple capabilities. The two most common
are handheld units and mobile units intended to be carried on a vehicle. Antennas are an
important consideration in choosing either type of GPS unit. Several designs are
available, and the one chosen should be suitable to the terrain in which it is to be most
often used. Also, because basic GPS is not as accurate as one might like, it is essential to
have a unit that is capable of differential GPS (DGPS) or of using the wide area
augmentation system (WAAS). A discussion of these methods is given in Chapter 2.
Global positioning system units are powered by a number of different sources, the
most common of which are batteries, including adapters for using the battery of a vehicle.
The batteries in handheld units can be either rechargeable or of the dry-cell type. Dry-cell
batteries can last up to 20 hr and many units have battery-saving features. One set of
batteries can thus last for a day or two of sampling. If sampling will take longer,
rechargeable batteries are preferred. If the person sampling is riding a vehicle with a 12-
V battery, a battery connector is preferred.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search