Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
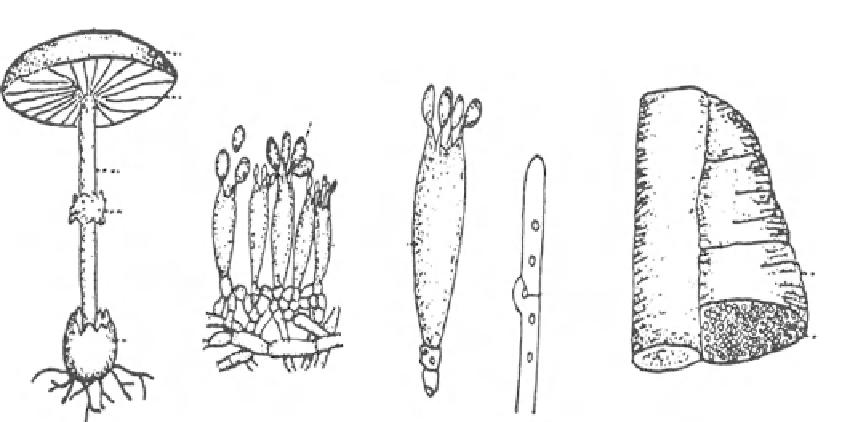
a
Pileus
b
Gill
Basidiospore
Stipe
Annulus
Basidium
Clamp
Connection
Conk
Pore
Volva
Fig. 4
Reproduction in Basidiomycetes. a, mushroom
(Agaricaceae) with cap of pileus lined with gills bearing
basidia germinating by basiodiospores. b, sporophore, or
conk, in Polyporaceae where basidia line pores instead of
gills. Mycelium in basidiomycetes sometimes have
a structure around a septum called a clamp connection
Ustilaginales
The smuts. Spore masses are usually black; spores
are heavy-walled chlamydospores, germinating
by a promycelium (basidium) and four or more
sporidia (basidiospores).
Ustilaginaceae Smuts. Basidiospores are pro-
duced on sides of a four-celled promycelium.
Tilletiaceae Smuts. Elongated basidiospores
produced in a cluster at
into four cells, each producing a single basidio-
spore on a sterigma; spore masses are yellowish
or orange, and there are several spore forms.
Melampsoraceae Teliospores sessile, in crusts,
cushions, or cylindrical masses, or solitary, or in
clusters, in mesophyll or epidermis of host. Now
placed in the order Melanosporales.
Pucciniaceae Teliospores usually stalked, sepa-
rate, or held together in gelatinous masses; some-
times several on common stalks; less frequently
sessile, catenulate, breaking apart.
Auriculariaceae Basidia with transverse septa;
typically gelatinous. The genus
Helicobasidium
causes
tip of a non-septate
promycelium or basidium.
Urediniomycetes
violet
root
rot
and
the
genus
Urediniomycetes - have cylindrical, often
slightly curved, transversely septate basidia.
Each cell forms a sterigma with a basidiospore,
which is forcibly discharged when mature. Usu-
ally basidia develop on resting spores called
teliospores. The Urediniomycetes contain two
orders, the Uredinales (rust fungi, obligate para-
sites on vascular plants) and the Auriculariales.
Herpobasidium
causes blight of
lilac. Now
placed in the order Auriculariales.
Septobasidiaceae (Felt fungus) Arid, lichenoid,
parasitic on scale insects; probasidia often with
thickened walls. Now placed in the order
Septobasidiales. There are six other families, of
no particular interest from the standpoint of plant
disease.
Uredinales
The rusts. More than 5,000 species have been
described in about 300 genera. Always parasitic
in vascular plants; teliospores or probasidia ger-
minate with a promycelium divided transversely
Basidiomycetes
Basidiomycetes - About 10,000 species have
been described and includes the mushrooms and