Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
d
c
A
B
a
b
a
b
b
1
a
1
d
1
e
b
2
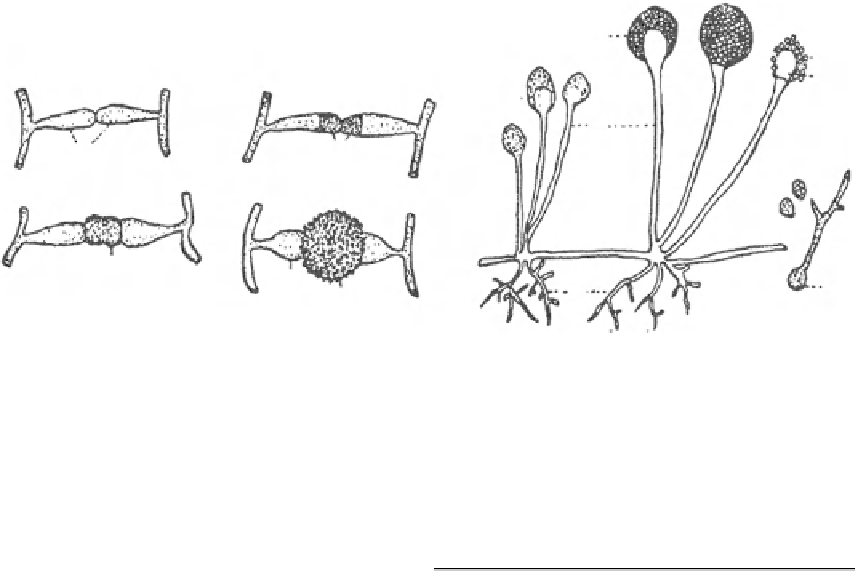
Fig. 2
Reproduction of a Zygomycete (
Rhyzopus
, order
Mucorales). A suspensors (
a
) from different hyphae cut
off gametes (
b
) ofequalsize which fuse (
b
1
) to form
a spinyzygospore (
b
2
). B asexualsporangiospores (
d
)
formed inside a sporangium (
a
) formed on
a sporangiophore (
b
) around a columella (
c
). Hyphae are
attached to substratum by rhizoids (
e
). Sporangiospore
germinates by a germ tube (
d
1
)
usually formed and dispersed by air. There are two
classes, the Zygomycetes, and the Trichomycetes
(mainly parasitic on insects). These classes differ by
morphological and chemical characteristics.
as conidia; zoospores free within a gametangial
vesicle.
Ascomycota
The thalli may consist of aseptate yeast cells or
septate hyphae. Following meiosis, endogenous
spores (ascospores) form within a cell called an
ascus. There are three groups: Archiascomycetes
(members lack ascogenous hyphae and ascocarps,
and asci sometimes homologized with sporangia),
Saccharomycetales (Ascomycetes, Yeasts: contain
no ascogeneous hyphae and ascocarps; asci
thin walled and may release ascospores by deli-
quescing or breaking) and Filamentous Ascomy-
cetes (with functional sex organs - possess
ascogonium, ascogenous hyphae and crosiers that
become enclosed in an ascocarp). The asci in Asco-
mycetes are aggregated in fructifications called
ascomata (apothecia, cleistothecia, perithecia).
The asexual states (anamorphs) of the Ascomycetes
usually are classified in a separate class called
Deuteromycetes.
Zygomycetes
Mucorales
Profuse mycelium, much branched; asexual
reproduction by sporangia or conidia; sexual
reproduction by zygospores from union of two
branches of the same mycelium or from different
mycelia. Some species damage fruits and vegeta-
bles in storage. Only two families are of much
interest to plant pathologists.
Mucoraceae Sporangiophores liberated by
breaking up of thin sporangial wall; zygospores
rough.
Mucor
and
Rhizopus
cause storage molds.
Choanephoraceae Both sporangia and conidia
present, the latter borne on swollen tips; zygo-
spores naked.
Choanephora
is a weak parasite
causing blossom blight or blossom-end rot of
young fruits.
Ascomycetes
Entomophthorales
Profuse mycelium, species frequently parasitic
on insects or other animals, rarely on plants;
anamorph spores modified sporangia functioning
The diagnostic characteristics of this class are
a septate mycelium (hyphae with cross walls)