Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Alternaria
Botrytis
Cercospora
Entomosporium
Ovulinia
Septoria
Volutella
Pestalotia
Phomopsis
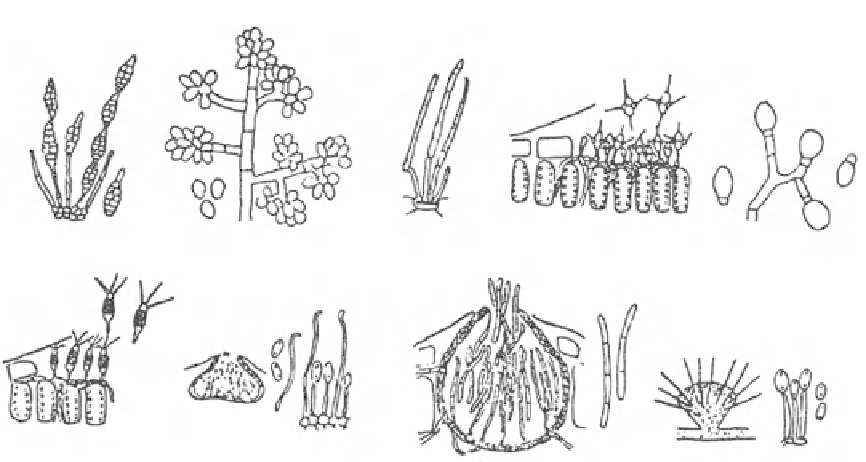
Fig. 1
Conidial Production Among Some Fungi Causing
Blights.
Alternaria
, dark muriform spores in chains;
Botrytis
, hyaline spores in clusters;
Cercospora
, pale to
dark septate spores on dark conidia protruding from sto-
mata;
Entomosporium
, peculiarly appendaged spores in
acervulus;
Ovulina
, hyaline spore with basal disjunctor
cell, borne free on mycelium;
Pestalotia
, in acervulus,
median cells colored, end cells hyaline, apical cell with
appendages;
Phomopsis
, oval and filiform hyaline spores
in pycnidium;
Septoria
, septate hyaline spores in Pycnid-
ium;
Volutella
, hyaline spores
formed on a hairy
sporodochium
yellow and brown; entire tops are killed in severe
infections. In California the disease is known as
late blight, with the peak coming in November.
The fungus apparently winters in discarded tops
and on seed.
Control
Clean up refuse. Spray with a fixed cop-
per spray or dust, starting soon after seedlings
emerge and repeating at 7-to 10-day intervals.
Alternaria dianthicola
Carnation Collar
Blight
,
Leaf Spot
,
Stem and Branch Rot
, general
on carnation, widespread on garden pinks and
sweet william. The chief symptom is a blight or
rot at leaf bases and around nodes, which are
girdled. Spots on leaves are ashy white but cen-
ters of old spots are covered with dark brown to
black fungus growth. Leaves may be constricted
and twisted, the tip killed. Branches die back to
the girdled area, and black crusts of spores are
formed on the cankers. Conidia are spread during
watering in the greenhouse or in rains, outdoors.
Entrance is through wounds, stomata, or directly
through the cuticle. The spores are carried on
cuttings.
Control
Commercial growers can often avoid
Alternaria blight by keeping plants growing con-
tinuously in the greenhouse. Cuttings should be
disease-free, taken from midway up the stem,
broken at the joint rather than cut, and started in
sterilized soil. Ordinarily the foliage should be
kept dry, but under mist propagation chemicals
introduced into the mist system have reduced
blight.
Alternaria helianthi
Blight
and
Stem Lesion
of
sunflower.
Alternaria panax
Alternaria Blight
,
Root Rot
,
Leaf Spot
of ginseng, ming aralia, and golden-
seal, generally distributed. In Ohio the disease
appears each year in semiepidemic form and has
been controlled with bordeaux mixture or a fixed
copper spray plus a wetting agent, starting when
plants emerge in early May and repeating every
2 weeks until 3 weeks after bloom.
Alternaria solani
Early Blight
of potato and
tomato, general on these hosts, occasional on
eggplant and pepper. The pathogen was first
described from New Jersey, in 1882.