Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Motivated by the presence of
and
, the gapping analysis in NLC'06 assumed
an intrapropositional coordination structure. This worked well for subject and
object gapping, in which a coordination may be defined between the different
verbs contained in the gapping parts. But what if the gapping parts do not
contain any verb because it is the verb that is gapped?
When we finally subjected verb gapping to a DBS graph analysis, the fol-
lowing solution was clear to see:
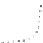
9.5.3 DBS
GRAPH ANALYSIS OF VERB GAPPING IN
9.5.2
(i) semantic relations graph (SRG)
(iii) numbered arcs graph (NAG)
10
8
11
eat
12
9
7
eat
1
4
6
Bob
apple
23
5
Bob
apple
(ii) signature
N
N
V
N
N
(iv) surface realiztion
1
Bob
2
3
4−5
6−7
8
9
10−11
12
.
ate
an_apple
Jim
a_pear
and
Bill
a_peach
For graphical reasons, the lines representing the subject verb and the object
verb relations in the gapping parts
Jim a pear
and
Bill a peach
are oriented
properly only when rotated (see the orientation of the writing). The n=7 signa-
ture has the degree sequence 6111111. The surface realization uses each arc in
the NAG once (no multiple visits), with empty traversals in 4, 6, and 10, and
double realizations in 3, 7, and 11.
The graph analysis 9.5.3 requires a proplet representation different from the
coordination-oriented solution of NLC'06, Sect. 8.5. Here the semantic re-
lations between the gapping constructions and the filler are run via the
arg
attribute of the lone verb and the
fnc
attributes of the nouns in the gapping
constructions - and not via their
nc
and
pc
attributes.













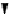
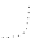
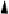


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search