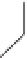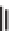Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
R
+
OP
2
O
6
-3
HO
C
5
H
11
geranyl-pyrophosphate
R=H: olivetol
R=COOH: olivetolic acid
R
HO
C
5
H
11
H
3
C
OH
OH
R
b
H
2
C
C
5
H
11
HO
OH
H
a
a
R=H: cannabigerol
R=COOH: cannabigerolic acid
b
OH
R'
OH
R
O
C
2
H
11
R"
C
2
H
11
HO
cannabinols
-
9
tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
R'=COOH; R'=H :
Δ
-
9
THC acid A
R'=H; R'=COOH :
Δ
-
9
THC acid B
R'=R''=H:
Δ
R=H: cannabidiol (CBD)
R=COOH: cannabidiolic acid
Fig. 3.12.
Diagrammatic representation of the biosynthesis of tetrahydrocannabinoids (THC) and
cannabidiol (CBD) (from Mechoulam and Hanus, 2002).
Monoterpenes
myrcene
limonene
Isoprene unit
Sesquiterpenes
OH
OH
OH
guaiol
β
-eudesmol
γ
-eudesmol
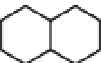
Fig. 3.13.
Structure of the principal terpenes of Cannabis.
products. These trace terpenes allow various
cultivars to be differentiated by quantitative
chemotaxonomic analysis (Novak
et al
., 2001;
Hillig, 2004).
THE FLAVONOIDS
.
Plant flavonoids are impor-
tant components, as they are responsible for
the pigmentation of both flowers and fruit and
are found throughout the plant (Harborne and