Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
EUROPE
UNITED STATES
12800
10500
5800
5100
4850
980
2080
4200
3400
750
1400
1040
PVC
PE
PP
Styrenes
Unsaturated polyesters (PEs)
Technical plastics
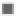
Fig. 14.1.
Consumption in kt.
The second notable difference is the lower
consumption of polypropylene (PP) and the
greater consumption of unsaturated polyesters
in the USA. This is due to the intensive use of
temperature-hardened plastics in the American
automobile industry.
Excluding technical plastics, polymers that
are reinforced easily represent a demand of 6
Mt, both in the USA and the EU.
and, in particular, their rigidity and traction.
Improvements to these parameters have been
achieved through the incorporation of reinforc-
ing materials.
Reinforcing materials are made of unwo-
ven fibres or from fabric. Single fibres can be
made from glass, carbon or from polymers
(aramid, PE, liquid crystal polymer (LCP)).
Since the beginning, glass fibre has been the
predominant fibre, with the other fibres mak-
ing their appearance only recently. The quan-
tity of fibres used across the world amounts to
some 2 Mt per annum; the quantity of natural
fibres used in the same way has not, however,
been quantified.
14.2.2 Reinforcing materials
The plasturgy industry has at its disposal a large
number of polymers suitable for transforma-
tion. These are produced by the chemical indus-
try, but as raw materials, do not possess the
technical properties required for the end prod-
uct to be constructed. In order to attain these
properties, the plastics manufacturer must
modify the polymers by incorporating various
additives, ingredients, adjuvants (stabilizers, pig-
ments and lubricants), reinforcing fibres, etc.
The rapid growth in demand for plastic
materials has led, in the space of a few dec-
ades, to polymer production that accounts for
close to 100 Mt of plastic per annum.
Concurrent with the growth in applica-
tions, the properties of the materials produced
have continued to improve. This has led to
them replacing traditional materials such as
metal, wood and glass.
One of the most significant developments
contributing to the increased use of plastic
materials has been, without doubt, the improve-
ments made to their mechanical properties
14.2.3
Composites and compounds
Historically, reinforcing fibres started being used
in the industrial manufacture of temperature-
hardened plastics. These are polymers with a
three-dimensional structure produced by a
chemical reaction between two or more mostly
liquid components. The structure of these mater-
ials produced by this chemical reaction cannot
subsequently be changed by heating. The fibre-
reinforced products obtained in this way are
generally described as 'composites'. Their most
important applications are in the manufacture
of automobile parts (body panels, bonnet, tail-
gate, wing…), in the leisure industry (boat hulls)
and in electrical engineering (fuse boxes), as well
as in the manufacture of body panels for agricul-
tural and specialist machinery that is produced
in relatively moderate quantities.