Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
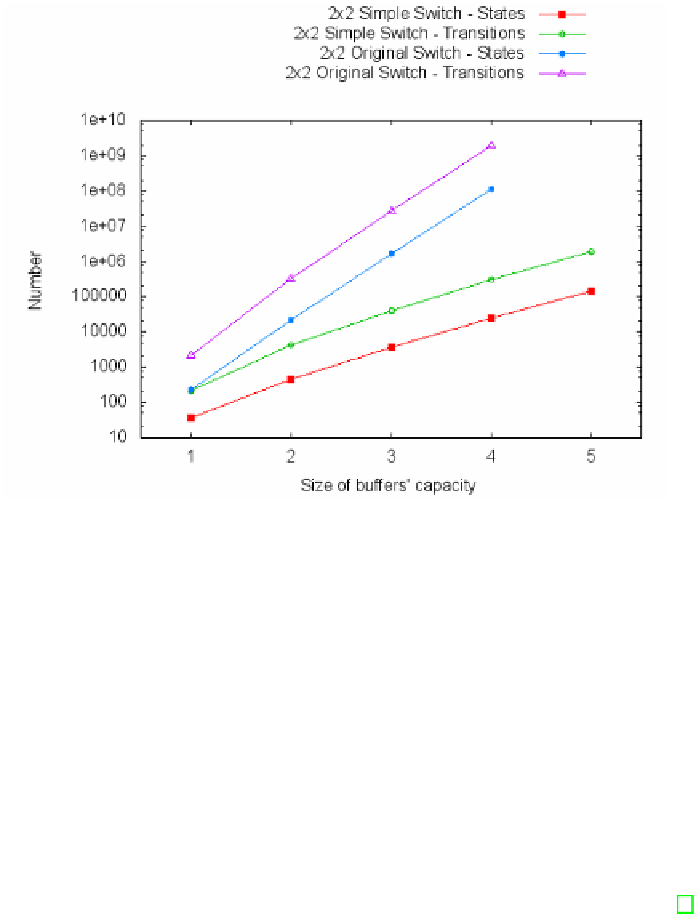
Fig. 1.
Complexity of the model expressed in number of states and transitions for the
simplified and original switch models
8 Conclusion and Future Work
In this paper, we have shown, in a case-study, that mCRL2 is suitable for the
modelling and subsequent analysis of a system in which multi-party communi-
cations combined with priority-based communication occur. We have tried to
apply local reasoning as much as possible, by generalizing the behavior of the
buffers by type, thereby preserving both the possibility to send prioritized pack-
ets as well as sending packets simultaneously. As a consequence, it is possible
to re-use the models in a more general setting. Furthermore, we showed that
with mCRL2, we were also able to verify some properties, that has led to an
increase in confidence that the model represents the design intent. Thereby, we
have shown that mCRL2 is at least comparable to the formalisms used in [6],
and in some cases more suitable for specifying complex system designs.
We should note that the comparison is based on subjective grounds. For a fair
comparison, one should study the possible language constructs for each of the
formalisms and point out the differences. This requires an expert over multiple
formalisms or a cooperation among experts of different formalisms. Since the case
study is centered around a specific specification, for which the models are created
according to the level of expertise of the designers, the outcome of the comparison
is subjective. As the authors of this paper can be considered experts when it
comes to mCRL2 specifications, and are familiar with ACP and Statecharts, we
are confident about the claims made between these formalisms.