Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
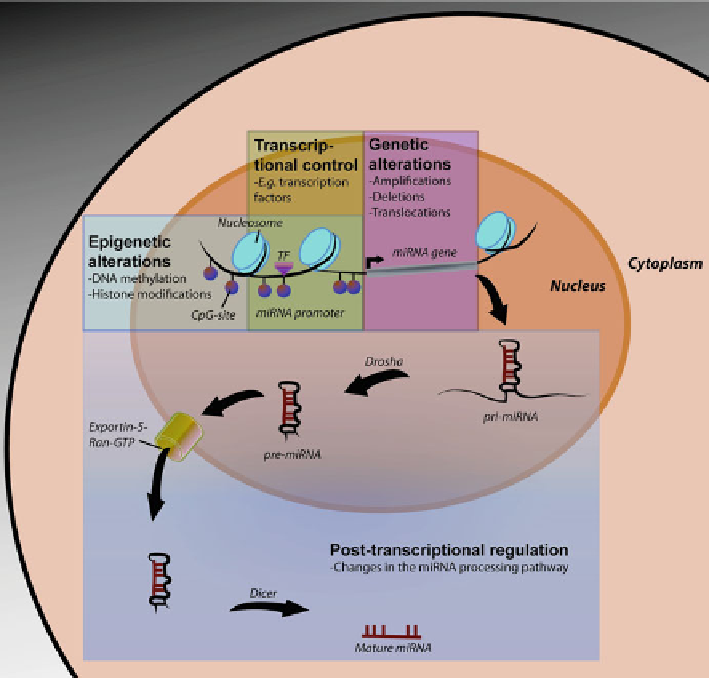
Fig. 13.1
Mechanism of miRNA deregulation
. The regulation of miRNA expression is a tightly
regulated process and many alterations might contribute to the change in expression levels of a
mature miRNA in cancer. The major mechanisms of miRNA regulation can be divided into four
groups. (1,
red box
): Genomic (genetic) alterations, such as deletions, amplifications, or transloca-
tions of the miRNA gene, resulting in abnormal miRNA gene copy number. (2,
green box
):
Changes in the transcriptional control of the miRNA, e.g., altered levels of important transcription
factors (TF). (3,
blue box
): Epigenetic alterations like DNA methylation of CpG sites and various
covalent modifications of histone proteins in nucleosomes. (4,
purple box
): Post-transcriptional
mechanisms such as modulations in the expression and activity of the miRNA processing enzymes,
e.g., Drosha, Exportin-5, and Dicer
Changes in miRNA expression in cancer might also be attributable to posttran-
scriptional control, such as impairment of miRNA processing steps. Key proteins in
the processing pathway of miRNAs may be deregulated or dysfunctional in cancer,
and can enhance cancer development further [
80
]. For instance, a mutation in the
exportin-5 gene (XPO5) can lead to accumulation of pre-miRNAs in the nucleus of
cells [
81
]. Furthermore, editing of the mature miRNA has been shown to change
miRNA complementarity to the target sequences [
82-
84
] .
Search WWH ::

Custom Search