Database Reference
In-Depth Information
traditional features of recommender systems, Yelp provides social network features
so that it can attract more users. Specifically, Yelp allows users to invite their
friends to join Yelp or make new friends with those who already exist at Yelp. The
friendship at Yelp is a mutual relationship, which means that when a user adds
another user as a friend, the first user will be automatically added as a friend of the
second user. Yelp provides a homepage for each local commercial entity and each
user. From the homepage of a local entity, we can find all the reviews of this entity.
From the homepage of a user, we can find all the reviews written by this user, as
well as friends explicitly specified by this user.
Specifically, we picked restaurants, the most popular category at Yelp, as the
problem domain. We crawled the homepages of all the Yelp restaurants in the Los
Angeles area that were registered before November 2007, which ended up being
4,152 restaurants. Then, by following the reviewers' links in the Yelp restaurant
homepages, we further crawled the homepages of all these reviewers, which
resulted in 9,414 users. Based on the friend links in users' homepages, we were
able to identify friends from the crawled users and thus reconstruct a social network
of Yelp users. Note that the friends we collected for each user may only be a subset
of the actual friends listed on the user's homepage. This is because we require every
user in our dataset to have at least one review in the crawled restaurants. In other
words, the social network that we crawled has a focus on dining.
A preliminary study of this dataset yields the following results. The dataset
contains 4,152 restaurants, 9,414 users, and 55,801 user reviews. Thus, each Yelp
user, on average, writes 5.93 reviews and each restaurant, on average, has 13.44
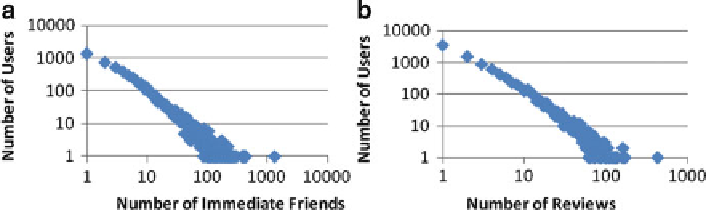
reviews. If we take a closer look at the relations between the number of users and the
number of their immediate friends (as shown in Fig.
4.1a
), we can see that it actually
follows a
power-law distribution
; this means that most users have only a few
immediate friends while a few users have a lot of immediate friends. A similar
distribution also applies to the relations between the number of users and the number
of reviews, as shown in Fig.
4.1b
. Because most users on Yelp review only a few
restaurants, it thus causes a data sparsity issue as in most recommender systems. In
particular, the sparsity of this dataset, i.e., the percentage of user/item pairs whose
ratings are unknown, is 99.86%.
Fig. 4.1 (a) The number of users versus the number of immediate friends in the Yelp network, and
(b) the number of users versus the number of reviews both follow the power-law distribution
Search WWH ::

Custom Search