Database Reference
In-Depth Information
It has taken years to put the components together that comprise the Semantic
Web, including the standardisation of RDF, the W3C release of the Web Ontology
Language (OWL) and standardisation on SPARQL, which adds querying capabil-
ities to RDF. So with standards and languages in place, we can see Semantic Web
technologies being used by early adopters.
Semantic Web technologies are popular in areas such as research and life
sciences where it can help researchers by aggregating data on different medicines
and illnesses that have multiple names in different parts of the world. On the Web,
Twine is offering a knowledge networking application that has been built with
Semantic Web technologies. The Joost online television service also uses Semantic
technology on the backend. Here, Semantic technology is used to help Joost users
understand the relationships between pieces of content, enabling them to find the
types of content they want most. Oracle offers a Semantic Web view of its Oracle
Technology Network, called the OTN Semantic Web, to name a few of those
companies who are implementing Semantic Web technologies.
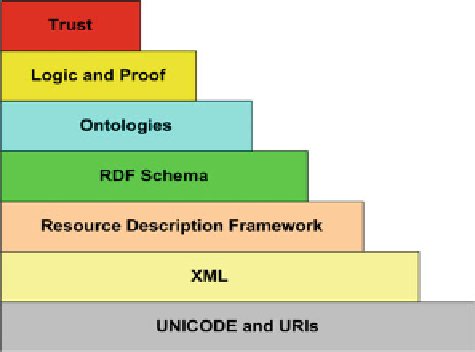
The architecture of the Semantic Web is shown in Fig.
10.1
. The seven layers are
as follows:
l
Unicode and URI
: Unicode, the standard for computer character representation,
and URIs, the standard for identifying and locating resources (such as pages on
the Web), provide a baseline for representing characters used in most of the
languages in the world and for identifying resources.
l
XML
: XML and its related standards, such as Namespaces and Schemas, form a
common means for structuring data on the Web, but without communicating the
meaning of the data. These are already well established within the Web.
l
RDF
: RDF is the first layer of the Semantic Web proper. RDF is a simple
metadata representation framework, using URIs to identify Web-based resources
and a graph model for describing relationships between resources. Several
syntactic representations are available, including a standard XML format.
Fig. 10.1
Semantic Web
layered architecture
Search WWH ::

Custom Search