Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
(Figure 1). Agriculture is mainly dominated by plantations of olive trees, which is the main
crop of the study area. The region has a Mediterranean climate with intensive precipitations
between January and May (600-900 mm). According to Darwish et al. (2005), the study area
was dominated by a well-drained red soil classified as an association of Gleyic and Vertic
Luvisols. The texture of the soil is clay (sand 24%, silt 20%, and clay 56%) with a calcium
carbonate reaching 22%. Despite its clay loamy texture, the red Mediterranean soil is
distinguished by a strong granular surface structure and porosity promoting intermediate and
high soil permeability (Darwish and Zurayk 1997). The organic matter content is low (1.3%).
Medium to coarse sub angular and angular blocky aggregates represent the strong structure of
the soil. Common fine to medium roots are also found. Common plants growing between
olive trees were of
Cichorium intybus
species.
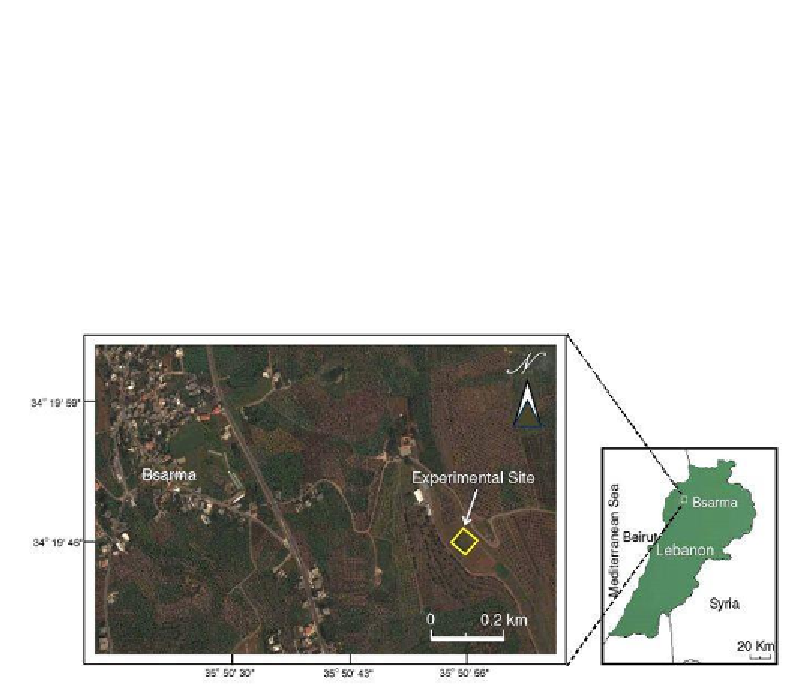
Figure 1. Experimental site localization map.
The field site consists of a land frame of about 256 m
2
. The study plot was divided into
24 separate parcels of 1 m
2
each spread over a surface of 49 m
2
and separated by distances of
75 cm (Figure 2). Each parcel was delimited with a wood frame of 1 × 1 × 0.15 m (length ×
width × height). To simulate the potential source of pollution originating from PF and PG-
amended soils, 12 parcels were used for PG application and 12 parcels for PF application as 1
kg and 2 kg of PG and PF respectively were dispersed on the soil surface in every parcel over
a surface of 0.5 m × 0.5 m, without homogenization with the soil. A reference parcel was left
without amendment.
The PF application quantity (2 kg) is equivalent of an intensity of 8 kg m
-2
(80,000 kg ha
-1
) application, about forty times higher than the fertilizer yearly use of 1860 kg
ha
-1
on arable soils in Lebanon (Farajalla et al. 2010). The purpose of this abundant
application was to subject the soil to leveraged state of influence induced by PFs application,
so as extreme ecological responses to such stimulus could be reached and measured.
Coring was carried out to a depth of 60 cm, using a high power (2,500 W) motor of type
Cobra TT. The core shaft used was 100 cm long, 6 cm in diameter. The first soil sample was
cored from the reference parcel labeled as R. Then, sample coring had been successively
performed in six different parcels labeled as PG1, PG2, PG3, PF1, PF2, and PF3 at six
Search WWH ::

Custom Search