Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
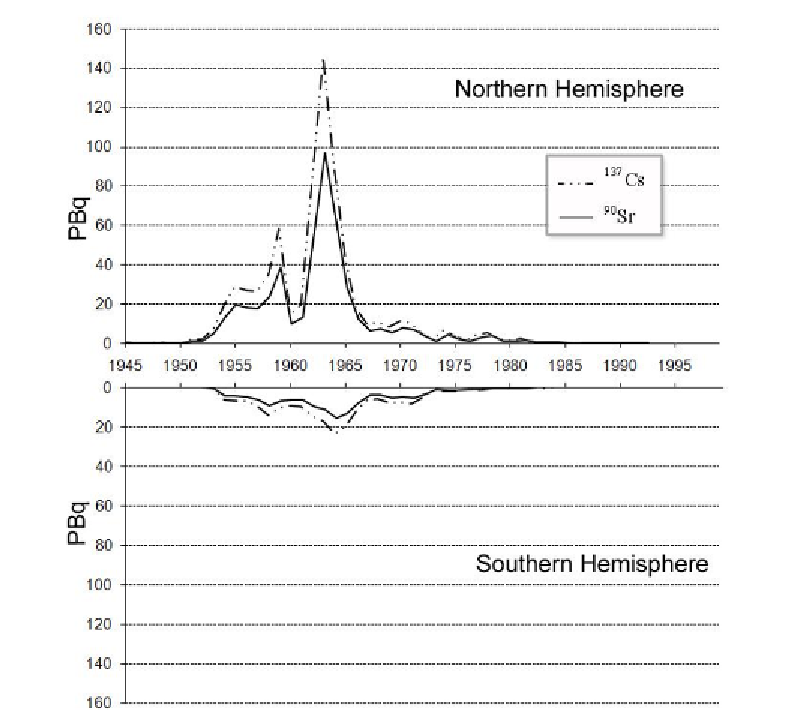
Figure 2. Annual deposition of
137
Cs and
90
Sr, expressed in petabecquerels (PBq), in the northern and
southern hemispheres produced by atmospheric nuclear tests. Data from UNSCEAR (UNSCEAR,
2000).
The deposition was inhomogeneous in latitude because of circulation patterns and
airflows in the stratosphere and troposphere. It was greater in the temperate regions, with a
maximum deposition of
90
Sr in the 40-50° latitude bands, and lower in the equatorial and
polar regions (UNSCEAR, 2000).
There is another natural series named neptunium (A = 4n+1), which was extinct because
the half-life of
237
Np (T
½
= 2.14·10
6
yr) is shorter than the Earth's age. However, it was re-
introduced into nature by the atmospheric release of anthropogenic
241
Pu (T
½
= 14.4 yr) and
241
Am (T
½
= 432.2 yr), predecessors of
237
Np.
Other sources of radionuclides in the environment are related to releases from nuclear
fuel reprocessing factories, plutonium fabrication plants, nuclear waste storage sites, and
accidents in nuclear reactors such as Windscale, Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and, more
recently, Fukushima. The most serious accident was Chernobyl (26 April 1986), which
marked a point of inflexion for radioecology and environmental radioprotection. Large
quantities of radionuclides were released, about 54, 85, and 10 PBq for
134
Cs,
137
Cs, and
90
Sr,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search