Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
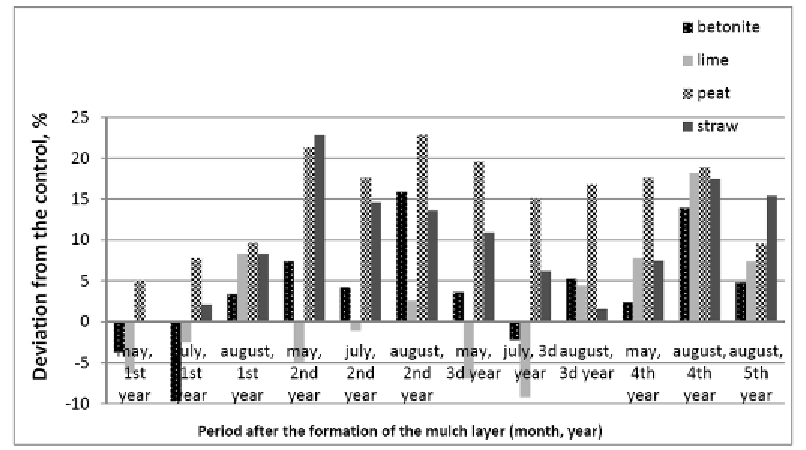
Figure 4. Effect of mulches on the content of organic matter in the plow horizon.
Peat has the highest rate of humification, which is significantly higher compared with
other types of organic fertilizers: straw, manure or green manure. The surface application of
peat contributed to further strengthening of the humification process. According to our data
and data from other literature, in the case of deep application the results similar to those we
had in our study are only achievable if the proportion is increased to 80-120 t/ha.
Straw also demonstrated high efficiency in improving the content of organic matter in the
soil. Its incorporation in the soil layer of 0-5 cm at the proportion of 5 t/ha increased organic
matter in the plow horizon by 223%, which exceeded the control (without mulches) by 10%
on average during the five years of observation (Figure 4).
Straw is the most common and cheapest source of organic matter in the soil. Dried straw
contains 84-86% of solids and 14-16% of water. The chemical composition of the dry
substance varies widely depending on the type of crops, weather and soil conditions. In
general, it has a high content of nitrogen-free compounds and a low content of protein
and ash.
It should be mentioned that in our experiments straw was added twice in the first and
fourth years of study. This is due to the fact that straw mineralizes very quickly when
incorporated at a shallow depth, so its action lasts only two or three years. This explains the
two peaks in the graph when the content of organic matter in the soil increased in the second
and fourth years of observation.
Applying a mulch layer of bentonite clay slightly increased organic matter in the topsoil
(Figure 4). Compared with the control, its amount grew by the average of 4.4 % at a high
confidence level during the five years. The increased humus content can be explained by the
stabilizing effect of clay minerals on organic matter. I. Lgotski (1979) found that bentonite
clay increases the accumulation of simple organic compounds, primarily fulvic acids from
humus. In our experiments, mixing 8 t/ha with the soil layer of 0-20 cm did not increase the
content of organic substances.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search