Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
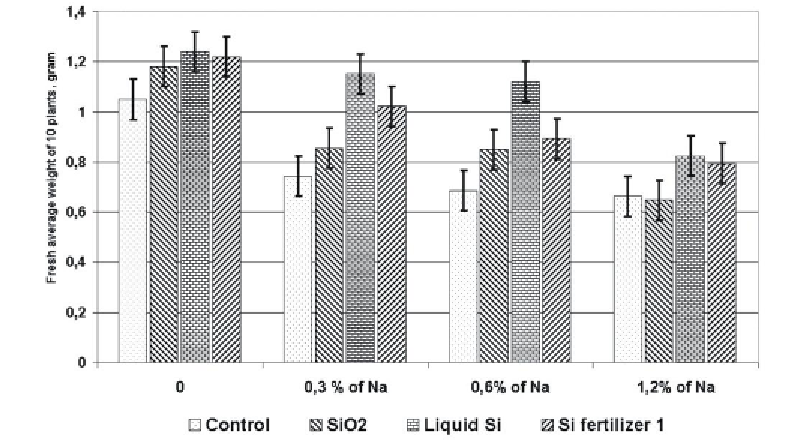
Figure 3. The effect of active Si on the plant salt tolerance of 3-week old barley (Matichenkov, 2008).
Our recent investigation has shown that soluble Si compounds can block or delay Na
transport in the apoplast. Monosilicic acid protects chlorophyll molecules against demolition
of them by Na (Matichenkov, 2008).
Silicon fertilizers are able to protect chemically plants against heavy metal toxicity
(Benavides et al., 2005).
Biochemical
Si plays an important part in all mechanisms described above. But some Si effects on
plant protection (for example, increasing frost tolerance) can't be explained by mechanical,
physiological or chemical processes. Additional mechanism was hypothesized to exist for the
synthesis of specific and non-specific stress-protectors in plant cell, which provided by
catalytic properties of polysilicic acid matrix (Biel et al., 2008). The additional pre-
suppositions for organic compounds synthesis on gels of polysilicic acids in living cell are the
following.
Active Si increases plant resistance against any type of stresses (Ma and Takahashi,
2002; Matichenkov et al., 2008; Matichenkov et al., 2011; Savant et al., 1997;
Snyder et al., 2006).
Any stress initiates increasing Si in plant tissue (Biel et al., 2008; Matichenkov,
2008; Matichenkov and Bocharnikova, 1994; Snyder et al., 2006).
Plant tissue contains high concentrations of mono- and poly-silicic acids
(Matichenkov et al., 2008).
Optimization of Si plant nutrition increases the antioxidants and stress-ferments
amounts in plant tissue (Biel et al., 2008; Matichenkov, 2008).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search