Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Application
Secondary
loop
Cooling
system
Electric
motor
Load
exchanger
Compressor
Expander
Compander
shaft
Air in
Core heat
exchanger
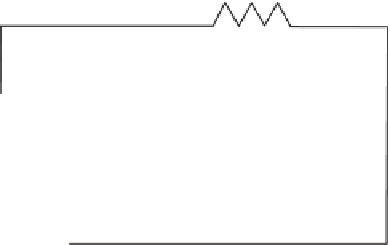
Figure 8.7
Closed-cycle air refrigeration equipment. Dry air is the working fluid that is recirculated in a
closed loop to avoid continuous dehumidification of the air.
From Pelsoci, 2001.
Some companies around the world are working in food refrigeration systems and freezing
systems for the food industry that can reach temperatures of 75°C below 0 by just using air
cycles.
Carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture
Carbon capture refers to the capture of carbon dioxide from point sources, such as power
plants and industries, with the purpose of reutilization or permanent storage. Carbon capture
and storage is an incipient concept that has not been proved completely yet. However, it is an
alternative that is being contemplated to keep burning fossil fuels without adding more carbon
dioxide to the atmosphere. Moreover, if carbon capture and storage is used in combination
with biofuels, the net result would be a sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere, or nega-
tive emissions.
When carbon dioxide comes from concentrated sources, for instance fermentations, its
capture is a relatively straightforward process. However, when the carbon dioxide is part of
combustion gases, capture is more complicated because it requires its separation from other
components first. Flue gas from coal-fired power plants contain between 10 and 12 percent
carbon dioxide by volume and the rest is mainly nitrogen and water vapor. Technologies
currently used to capture carbon dioxide from combustion gases are amine absorption in a